Fixed and variable costs: examples. Variable Cost Example
Almost every person dreams of quitting “working for someone else” and opening their own business, which will bring pleasure and a stable income. However, in order to become an aspiring entrepreneur, you will need to create a business plan containing a financial model of the future enterprise. Only this approach to business development will allow you to find out whether the investment in starting your own business can pay off.
In this article, we propose to learn about what fixed and variable expenses are and how they affect the profit of the enterprise.
Variable and fixed costs are the two main types of costs.
The importance of drawing up a financial model
Have you ever wondered why you need to draw up a business plan containing a financial model before starting your own business? Creating a business plan allows a novice entrepreneur to obtain information about the expected revenue of the enterprise, as well as determine fixed and variable costs. All these measures are aimed at choosing a strategy for developing the financial policy of the future business. The commercial component is one of basic principles successful enterprise. Economic theory says that finance is a benefit that should bring new benefits.
It is this theory that needs to be guided in the early stages of entrepreneurial activity. At the heart of every business is the rule that profit is the number one priority. Otherwise, your entire business model will turn into philanthropy. After we have made it a rule that working at a loss is unacceptable, we should move on to the financial model itself. Enterprise profit is the difference between income and production costs.
The latter are divided into two groups: variable and fixed expenses of the organization. In a situation where the level of expenses exceeds current income, the enterprise is considered unprofitable. The main task of entrepreneurial activity is to extract maximum benefits, subject to minimal use
Based on this, we can conclude that to increase income it is necessary to sell as many finished products as possible. However, there is another method of making a profit, which is to reduce production costs. Understanding this scheme is quite difficult, since the process of cost optimization has many different nuances. It is important to mention that these economic terms
, as “cost level”, “cost item” and “production costs” are synonymous. Let's look at all the types of manufacturing costs that exist.
Types of expenses All expenses of an organization are divided into two groups: variable and fixed costs.
This division helps to systematize the budgeting process, and also helps in planning a business development strategy. Fixed costs are expenses, the amount of which has no connection with the production capacity of the enterprise
 . This means that this amount does not depend on how much product is produced. Variable costs
. This means that this amount does not depend on how much product is produced. Variable costs - these are costs, the size of which changes in proportion to changes in the volume of production TO variable expenses
include conditionally fixed costs associated with business activities. Such expenses can change their properties and magnitude, depending on the impact of internal and external economic factors.
What do different types of expenses include? To the number fixed costs You can include the salaries of members of the enterprise administration, but only in a situation where these employees receive payments regardless of the financial condition of the organization. It is important to note that in
foreign countries managers gain income from their organizational skills by expanding the customer base and exploring new market areas. On Russian territory the situation is completely different. Most department heads receive high salaries, which are not tied to the effectiveness of their activities. This approach to organizing the production process leads to a loss of incentive to achieve best results. This is precisely what can explain the low productivity of labor indicators of many commercial institutions, since the desire to master new
technological processes at the top of the company is simply missing. Speaking about what fixed costs are, it should be mentioned that this item includes rent. Let's imagine small room. In this situation, the company administration must transfer a certain amount to the landlord monthly. This situation is considered standard, since it is quite difficult to recoup the purchase of real estate. Some small and middle class entities will require at least five years to return their invested capital.
It is this factor that explains that many entrepreneurs prefer to enter into an agreement to rent the necessary square meters. As mentioned above, rental costs are constant, since the owner of the premises is not interested in the financial condition of your company. For this person, all that is important is the timely receipt of payment specified in the contract.
Fixed expenses include depreciation costs. Any funds must be depreciated monthly until their initial cost is equal to zero. There are many in various ways adjustable depreciation current legislation.According to experts, there are more than a dozen various examples fixed costs. These include utility bills, payment for waste removal and recycling, and expenses for providing the conditions necessary for the implementation of labor activity. Key Feature such expenses is the ease of calculating both present and future costs.
 Fixed costs - costs, the value of which is almost independent of changes in the volume of production
Fixed costs - costs, the value of which is almost independent of changes in the volume of production The concept of “variable costs” includes those types of costs that depend on the proportional volume of goods manufactured. For example, consider a balance sheet item that contains an item related to raw materials and materials. In this paragraph you should indicate the amount of funds that the company will need for production purposes. As an example, consider the activities of a company engaged in the manufacture wooden pallets. To produce one unit of goods, you need to spend two squares of processed wood. This means that to make one hundred pallets, two hundred square meters of material will be required. It is these expenses that fall into the category of variables.
It should be noted that remuneration of employees may be part of both fixed and variable expenses.
- Similar cases are observed in the following situations:
- Employee salaries are interest rate, which depends on various deviations in the production process.
Under these conditions, it is very difficult to make a forecast about the necessary expenses in order to pay salaries to employees, since its volume will depend on many different factors. The division of expenses into constant and variable is carried out in order to analyze the profitability of the enterprise, as well as determine the degree of unprofitability of the production process.
It should be noted that any production activity of a company consumes various energy resources. These resources include fuel, electricity, water and gas. Since their use is an integral part of production, an increase in the volume of output leads to an increase in the costs of these resources.
What are fixed and variable costs used for? One of the goals of this cost classification is to optimize production costs.
Taking into account such details when creating a financial model of an enterprise allows you to identify those positions that can be reduced to supplement income. Also, such data will help you find out how cost reduction will affect the production capacity of the enterprise. Below we propose to consider constant and variable costs examples based on a manufacturing organization kitchen furniture . To carry out production activities, the management of such a company needs to invest funds in paying for the lease agreement, utility costs, depreciation costs, purchase Supplies
 and raw materials, as well as employee salaries. After a list of general expenses has been compiled, all items on this list should be divided into variable and fixed costs.
and raw materials, as well as employee salaries. After a list of general expenses has been compiled, all items on this list should be divided into variable and fixed costs. Knowledge and understanding of the essence of fixed and variable costs is very important for competent business management The category of fixed expenses includes depreciation costs, as well as salaries of the enterprise administration, including the accountant and director of the company. In addition, this item includes expenses for payment electrical energy , used to illuminate the room. Variable costs include the purchase of raw materials and consumables necessary for the production of an incoming order. In addition, this item includes expenses for utility bills, since some energy resources are used only in the production process itself. This category can include employees involved in the furniture manufacturing process, since the rate directly depends on the volume of products produced. Transportation costs are also included in the category of variable financial costs of the organization.
How production costs affect the cost of goods
After it was created financial model future enterprise, it is necessary to analyze the influence of variable and fixed costs on the cost of manufactured goods. This allows you to reorganize the company's activities in order to optimize the production process. Such an analysis will help you understand how many personnel will be required to complete a particular task.
 Dividing costs into fixed and variable is one of the most important tasks of financial departments of companies
Dividing costs into fixed and variable is one of the most important tasks of financial departments of companies Such a plan allows you to determine the required level of investment in the development of the organization. You can reduce the cost of energy resources by using alternative sources, as well as by purchasing more modernized equipment with a high coefficient useful action. Next, it is recommended to analyze variable expenses in order to determine their dependence on external factors. These actions will help identify those costs that can be calculated.
All of the above actions allow us to better understand the cost structure of the enterprise, which allows us to modify the organization’s activities in accordance with the chosen development strategy. The main goal is to reduce the cost of manufactured goods in order to increase the number of products sold.
It is impossible for companies to carry out any activity without investing costs in the process of making a profit.
However, there are costs different types. Some operations during the operation of the enterprise require constant investments.
But there are also costs that are not fixed costs, i.e. refer to variables. How do they affect the production and sale of finished products?
The concept of fixed and variable costs and their differences
The main goal of the enterprise is the manufacture and sale of manufactured products to make a profit.
To produce products or provide services, you must first purchase materials, tools, machines, hire people, etc. This requires the investment of various amounts of money, which are called “costs” in economics.
 Since monetary investments in production processes come in many different types, they are classified depending on the purpose of using the expenses.
Since monetary investments in production processes come in many different types, they are classified depending on the purpose of using the expenses.
In economics costs are shared according to the following properties:
- Explicit is a type of direct cash costs for making payments, commission payments to trading companies, payment for banking services, transportation costs, etc.;
- Implicit, which includes the cost of using the resources of the organization's owners, not provided for by contractual obligations for explicit payment.
- Fixed investments are investments to ensure stable costs during the production process.
- Variables are special costs that can be easily adjusted without affecting operations depending on changes in production volumes.
- Irreversible - a special option for spending movable assets invested in production without return. These types of expenses occur at the beginning of the release of new products or reorientation of the enterprise. Once spent, funds can no longer be used to invest in other business processes.
- Average are estimated costs that determine the amount of capital investment per unit of output. Based on this value, the unit price of the product is formed.
- Marginal is the maximum amount of costs that cannot be increased due to the ineffectiveness of further investments in production.
- Returns are the costs of delivering products to the buyer.
Of this list of costs, the most important are their fixed and variable types. Let's take a closer look at what they consist of.
Kinds
What should be classified as fixed and variable costs? There are some principles by which they differ from each other.
 In economics characterize them as follows:
In economics characterize them as follows:
- Fixed costs include the costs that need to be invested in the manufacture of products within one production cycle. For each enterprise they are individual, therefore they are taken into account by the organization independently based on analysis production processes. It should be noted that these costs will be characteristic and the same in each of the cycles during the manufacture of goods from the beginning to the sale of products.
- variable costs that can change in each production cycle and are almost never repeated.
Fixed and variable costs make up the total costs, summed up after the end of one production cycle.
If you have not yet registered an organization, then easiest way do this using online services, which will help you generate all the necessary documents for free: If you already have an organization, and you are thinking about how to simplify and automate accounting and reporting, then the following online services will come to the rescue, which will completely replace an accountant in your company and save a lot money and time. All reporting is generated automatically, signed electronically and sent automatically online. It is ideal for individual entrepreneurs or LLCs on the simplified tax system, UTII, PSN, TS, OSNO.
Everything happens in a few clicks, without queues and stress. Try it and you will be surprised how easy it has become!
What applies to them
Main characteristics fixed costs is that they do not actually change over a period of time.
In this case, for an enterprise that decides to increase or decrease its output, such costs will remain unchanged.
Among them can be attributed the following cash costs:
- communal payments;
- building maintenance costs;
- rent;
- employee earnings, etc.
In this situation, you should always understand that the constant amount of total costs invested in certain period time to release products in one cycle will only be for the entire number of products released. When calculating such costs individually, their value will decrease in direct proportion to the increase in production volumes. For all types of production this pattern is an established fact. 
Variable costs depend on changes in the quantity or volume of products produced.
To them include the following expenses:
- energy costs;
- raw materials;
- piecework wages.
These monetary investments are directly related to production volumes, and therefore change depending on the planned parameters of production.
Examples
In each production cycle there are cost amounts that do not change under any circumstances. But there are also costs that depend on production factors. Depending on these characteristics economic costs for a certain, short period of time are called constants or variables.
For long-term planning, such characteristics are not relevant, because sooner or later all costs tend to change.
Fixed costs are costs that do not depend in the short term on how much the company produces. It is worth noting that they represent the costs of its constant factors of production, independent of the number of goods produced.
Depending on the type of production into fixed costs consumables include:

Any costs that are not related to production and are the same in the short term of the production cycle can be included in fixed costs. According to this definition, it can be stated that variable costs are those expenses invested directly in product output. Their value always depends on the volume of products or services produced.
Direct investment of assets depends on the planned quantity of production.
Based on this characteristic, to variable costs The following costs include:
- raw material reserves;
- payment of remuneration for the labor of workers involved in the manufacture of products;
- delivery of raw materials and products;
- energy resources;
- tools and materials;
- other direct costs of producing products or providing services.

The graphical representation of variable costs displays a wavy line that smoothly rises upward. Moreover, with an increase in production volumes, it initially rises in proportion to the increase in the number of products produced, until it reaches point “A”.
Then cost savings occur during mass production, and therefore the line rushes upward at no less speed (section “A-B”). After the violation of the optimal expenditure of funds in variable costs after point “B”, the line again takes a more vertical position.
The growth of variable costs may be affected by irrational use funds for transport needs or excessive accumulation of raw materials, volumes of finished products during a decrease in consumer demand.
Calculation procedure
Let's give an example of calculating fixed and variable costs. The production is engaged in the manufacture of shoes. The annual production volume is 2000 pairs of boots.
 The enterprise has the following types of expenses per calendar year:
The enterprise has the following types of expenses per calendar year:
- Payment for renting the premises in the amount of 25,000 rubles.
- Interest payment 11,000 rubles. for a loan.
Production costs goods:
- for labor costs for the production of 1 pair 20 rubles.
- for raw materials and materials 12 rubles.
It is necessary to determine the size of total, fixed and variable costs, as well as how much money is spent on making 1 pair of shoes.
As we can see from the example, only rent and interest on the loan can be considered fixed or fixed costs.
Due to fixed costs do not change their value when production volumes change, then they will amount to the following amount:
25000+11000=36000 rubles.
The cost of making 1 pair of shoes is considered a variable cost. For 1 pair of shoes total costs amount to the following:
20+12= 32 rubles.
Per year with the release of 2000 pairs variable costs in total are:
32x2000=64000 rubles.
Total costs are calculated as the sum of fixed and variable costs:
36000+64000=100000 rubles.
Let's define average of total costs, which the company spends on sewing one pair of boots:
100000/2000=50 rubles.
Cost analysis and planning
 Each enterprise must calculate, analyze and plan costs for production activities.
Each enterprise must calculate, analyze and plan costs for production activities.
Analyzing the amount of expenses, options for saving funds invested in production are considered in order to rational use. This allows the company to reduce production and, accordingly, set a cheaper price for finished products. Such actions, in turn, allow the company to successfully compete in the market and ensure constant growth.
Any enterprise should strive to save production costs and optimize all processes. The success of the development of the enterprise depends on this. Thanks to the reduction in costs, the company's income increases significantly, which makes it possible to successfully invest money in the development of production.
Costs are planned taking into account calculations of previous periods. Depending on the volume of products produced, an increase or decrease in variable costs for the manufacture of products is planned.
Display in the balance sheet
In the financial statements, all information about the costs of the enterprise is entered into (Form No. 2).
Preliminary calculations during the preparation of indicators for entry can be divided into direct and indirect costs. If these values are shown separately, then we can assume that indirect costs will be indicators of fixed costs, and direct costs will be variable, respectively.
It is worth considering that the balance sheet does not contain data on costs, since it reflects only assets and liabilities, and not expenses and income.
To learn what fixed and variable costs are and what applies to them, see the following video:
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
Fixed costs: details for an accountant
- Operating leverage in the main and paid activities of accounting
The limit (threshold) does not cause an increase in fixed costs. Operating leverage (operating leverage) shows... changes in the volume of services provided. Conditionally fixed costs are costs whose value is... let's look at an example. Example 1 Fixed costs educational institution amount to 16 million... the threshold at which an increase in fixed costs will be required. In a favorable macroeconomic environment... activity) increases; in conditions of constant fixed costs, the BU receives savings (profit);
- ...
Financing government tasks: examples of calculations
- And contributions to funds). Conditionally fixed costs include general production and general business expenses... examples. At the same time, variable and fixed costs in relation to profit taxation resemble...
Does it make sense to divide costs into variable and fixed?
- Variable indirect costs and part of the fixed costs, depending on the utilization rate... the level of recovery of fixed costs and profit generation. When fixed costs are equal and the amount... between production volume, variable and fixed costs. The break-even point can be... simple direct costing; fixed (conditionally fixed) costs are collected on complex accounts (... not variable and fixed costs. There are the following options for distributing fixed costs for a specific...
Dynamic (temporal) profitability threshold model
- ... “German Metallurgy” was the first to mention the concepts of “fixed costs”, “variable costs”, “progressive costs”, ... ∑ FC – total fixed costs corresponding to the output of Q units of product... The following can be seen from the graph. Fixed costs FC change according to changes in intensity... R), respectively, total costs, fixed costs, variable costs and sales. The above... the period of sale of goods. FC – fixed costs per unit of time, VC – ...
It is formed as a function of variable and fixed costs, and therefore in marginal variables... (thousand rubles per unit of goods);
- – fixed costs (in thousand rubles);
– variable costs... the composition of costs includes such a component as fixed costs, which I already mentioned... in the cost of goods there are fixed costs, then the graph in Fig. 11... did not take into account the presence of fixed costs), and this causes...
- Current strategic and tactical tasks of the enterprise management team
Sales of products); fixed and semi-fixed costs for the production and sale of products... products; Zpos - fixed and semi-fixed costs of an enterprise for production. If... conditionally variable, fixed and conditionally fixed costs for the production of a unit of product or..., as well as fixed and conditionally fixed costs for the production and sale of products...
- Director's questions to which the chief accountant should know the answers
Its definitions are equal: revenue = fixed costs + variable costs + operating profit. We... in units = fixed costs/(price - variable costs/unit) = fixed costs: contribution margin per... units = (fixed costs + target profit) : (price - variable costs/unit) = (fixed costs + target profit... price. This means that the equation is valid: price = ((fixed costs + variable costs + target profit)/ target...
- What do you know about factory overhead?
The type of goods excluding conditionally fixed costs is equal to 2,000,000 rubles...
- Features of pricing during a crisis
The service must cover variable and fixed costs, as well as provide an acceptable level... unit of service; 3 post – semi-fixed costs for the entire volume of services; Profit... costs, at which fixed costs and profits are not covered - although... apply this tactic, since part of the fixed costs of the AU is borne by the founder. Below... – 144 thousand rubles. in year; fixed costs for paid groups – 1,000 ... organizations. Absence or low fixed costs. While business...
- Economic and social consequences of underutilization of the production and commercial capabilities of an enterprise
Production and sales. As part of fixed costs, highlight as separate items the items "... costs PerOut Marginal profit Profit Margin Fixed costs including: PostOutput Depreciation... Interest on loans ProcCr Other fixed costs PrPostOut Profit from core activities...
- Analysis of the financial condition of the company. Chapter II. Analysis of financial condition using the example of a manufacturing enterprise
Additional financial resources. The fixed charge coverage ratio is derived similar... than the interest coverage ratio). Fixed costs include interest and long-term rental... as follows: Fixed cost coverage ratio = EBIT (32) + "Rent payments" (30 ... in 1993. Kovoplast's fixed cost coverage ratio decreased in 1993 ...
- Rationalized information system for analysis and control of the main results of the enterprise
Orff products Fixed and semi-fixed costs for production and sales of products...
- Construction of management accounting based on IFRS reporting
Direct and indirect, variable and fixed costs), correct identification of the so-called drivers...
Which it was created. Variable and fixed costs If we break down the financial support formula... per unit of services; Post 3 – fixed costs. This formula is based on the assumption... basic staff pay). The amount of semi-fixed costs when the volume of services changes remains... in quantity. Therefore, the founder’s coverage of part of the fixed costs of accounting can be qualified as non-market... property. How reasonable is this allocation of fixed costs? From the position of the state, this is fair...
The size of which depends on the intensity of production. Variable costs are the opposite fixed costs. The key feature by which variable costs are identified is their disappearance when production is suspended.
What are variable costs?
Variable costs include the following:
- Piece-rate wages for workers tied to personal results.
- Expenses for the purchase of raw materials and components for production maintenance.
- Interest and bonuses paid to consultants and sales managers based on the results of plan implementation.
- The amount of taxes based on production and sales volumes. These are the following taxes: VAT, excise taxes, according to the simplified tax system.
- Expenses for paying for the services of service organizations, for example, goods transportation services or sales outsourcing.
- The cost of fuel and electricity consumed directly in the workshops. An important distinction is made here: the energy used in administrative buildings and offices - these are fixed costs.
Break-even point and types of variable costs
The value of VC varies in proportion to the size of total costs. When determining the break-even point, it is assumed that variable costs are proportional to production volume:
However, this is not always the case. An exception may be, for example, the introduction of a night shift. Since the night is higher, variable costs will increase at a greater rate than production volumes. Based on this feature, there are three types of VC:
- Proportional.
- Regressive variable - costs increase at a slower rate than. This effect is known as “economy of scale.”
- Progressive-variable - the rate of cost growth is higher.
Calculation of VC indicator
The classification of costs into fixed and variable is not used at all for accounting(there is no line “variable costs” in the balance sheet), but for management analysis. Calculation of variable costs is advisable because it gives the manager the opportunity to manage the profitability and profitability of the organization.
To determine the value of variable costs, methods such as algebraic, statistical, graphical, regression-correlation and others are used. The most famous and widespread is the algebraic method, according to which the following formula can be used to determine the value of VC:

Algebraic analysis assumes that the subject of the study has such information as the volume of production in physical terms (X) and the size of the corresponding costs (Z) for at least two points of production.
Also often used margin method, based on the definition of magnitude marginal income, which is the difference between the organization's profit and total variable costs.
Breaking point: how to minimize variable costs?
A popular strategy for minimizing variable costs is to determine " points fracture" - such a volume of production at which variable costs stop increasing proportionally and reduce the growth rate:

There may be several reasons for this effect. Among them:
- 1. Reducing labor costs for management personnel.
- 2. Application of a focusing strategy, which consists of increasing the specialization of production.
- 4. Integration of innovative developments into the production process.
Stay up to date with everyone important events United Traders - subscribe to our
Let's consider the variable costs of an enterprise, what they include, how they are calculated and determined in practice, consider methods for analyzing the variable costs of an enterprise, the effect of changing variable costs at different volumes of production and their economic meaning. In order to easily understand all this, an example of variable cost analysis based on the break-even point model is analyzed at the end.
Variable costs of the enterprise. Definition and their economic meaning
Variable costs of the enterprise (EnglishVariableCost,V.C.) are the costs of the enterprise/company, which vary depending on the volume of production/sales. All costs of an enterprise can be divided into two types: variable and fixed. Their main difference is that some change with increasing production volume, while others do not. If the company's production activities cease, then variable costs disappear and become equal to zero.
Variable costs include:
- The cost of raw materials, materials, fuel, electricity and other resources involved in production activities.
- Cost of manufactured products.
- Wages of working personnel (part of the salary depends on the standards met).
- Percentages on sales to sales managers and other bonuses. Interest paid to outsourcing companies.
- Taxes that have a tax base based on the size of sales and sales: excise taxes, VAT, unified tax on premiums, tax according to the simplified tax system.
What is the purpose of calculating the variable costs of an enterprise?
For any economic indicator, coefficient and concept, one should see their economic meaning and the purpose of their use. If we talk about the economic goals of any enterprise/company, then there are only two of them: either increasing income or reducing costs. If we summarize these two goals into one indicator, we get the profitability/profitability of the enterprise. The higher the profitability/profitability of an enterprise, the greater its financial reliability, the greater the opportunity to attract additional borrowed capital, expand its production and technical capacities, increase intellectual capital, increase its value in the market and investment attractiveness.
The classification of enterprise costs into fixed and variable is used for management accounting, and not for accounting. As a result, there is no such item as “variable costs” in the balance sheet.
Determining the size of variable costs in the overall structure of all enterprise costs allows you to analyze and consider various management strategies for increasing the profitability of the enterprise.
Amendments to the definition of variable costs
When we introduced the definition of variable costs/costs, we were based on a model of linear dependence of variable costs and production volume. In practice, variable costs often do not always depend on the size of sales and output, so they are called conditionally variable (for example, the introduction of automation of part of the production functions and, as a result, a reduction in wages for the production rate of production personnel).
The situation is similar with fixed costs; in reality, they are also semi-fixed and can change with production growth (increasing rent for industrial premises, changes in the number of personnel and the consequence of wages. You can read more about fixed costs in my article: “”.
Classification of enterprise variable costs
In order to better understand how to understand what variable costs are, consider the classification of variable costs according to various criteria:
Depending on the size of sales and production:
- Proportional costs. Elasticity coefficient =1. Variable costs increase in direct proportion to the growth of production volume. For example, production volume increased by 30% and costs also increased by 30%.
- Progressive costs (analogous to progressive-variable costs). Elasticity coefficient >1. Variable costs have a high sensitivity to change depending on the size of output. That is, variable costs increase relatively more with production volume. For example, production volume increased by 30% and costs by 50%.
- Degressive costs (analogous to regressive-variable costs). Elasticity coefficient< 1. При увеличении роста производства переменные издержки предприятия уменьшаются. Данный эффект получил название – «эффект масштаба» или «эффект массового производства». Так, например, объем производства вырос на 30%, а при этом размер переменных издержек увеличился только на 15%.
The table shows an example of changes in production volume and the size of variable costs for their various types.
According to statistical indicators, there are:
- Total variable costs ( EnglishTotalVariableCost,TVC) – include the totality of all variable costs of the enterprise for the entire range of products.
- Average Variable Cost (AVC) AverageVariableCost) – average variable costs per unit of product or group of goods.
According to the method of financial accounting and attribution to the cost of manufactured products:
- Variable direct costs are costs that can be attributed to the cost of goods manufactured. Everything is simple here, these are the costs of materials, fuel, energy, wages, etc.
- Variable indirect costs are costs that depend on the volume of production and it is difficult to assess their contribution to the cost of production. For example, during the industrial separation of milk into skim milk and cream. Determining the amount of costs in the cost price of skim milk and cream is problematic.
In relation to the production process:
- Production variable costs - costs of raw materials, supplies, fuel, energy, wages of workers, etc.
- Non-production variable costs are costs not directly related to production: commercial and administrative expenses, for example: transportation costs, commission to an intermediary/agent.
Formula for calculating variable costs/expenses
As a result, you can write a formula for calculating variable costs:
Variable costs = Costs of raw materials + Materials + Electricity + Fuel + Bonus part of salary + Interest on sales to agents;
Variable costs= Marginal (gross) profit – Fixed costs;
The combination of variable and fixed costs and constants constitute the total costs of the enterprise.
Total costs= Fixed costs + Variable costs.
The figure shows the graphical relationship between enterprise costs.

How to reduce variable costs?
One strategy for reducing variable costs is to use “economies of scale.” With an increase in production volume and the transition from serial to mass production, economies of scale appear.
Economies of scale graph shows that as production volume increases, a turning point is reached when the relationship between costs and production volume becomes nonlinear.

At the same time, the rate of change in variable costs is lower than the growth of production/sales. Let's consider the reasons for the appearance of the “production scale effect”:
- Reducing management personnel costs.
- Use of R&D in production. An increase in output and sales leads to the possibility of conducting expensive scientific research research work to improve production technology.
- Narrow product specialization. Focusing the entire production complex on a number of tasks can improve their quality and reduce the amount of defects.
- Production of products similar in the technological chain, additional capacity utilization.
Variable costs and break-even point. Example calculation in Excel
Let's consider the break-even point model and the role of variable costs. The figure below shows the relationship between changes in production volume and the size of variable, fixed and total costs. Variable costs are included in total costs and directly determine the break-even point. More
When the enterprise reaches a certain volume of production, an equilibrium point occurs at which the size of profits and losses coincides, net profit is equal to zero, and marginal profit is equal to fixed costs. Such a point is called break-even point, and it shows the minimum critical level of production at which the enterprise is profitable. In the figure and calculation table presented below, 8 units are achieved by producing and selling. products.

The enterprise's task is to create security zone and ensure a level of sales and production that would ensure the maximum distance from the break-even point. The further the enterprise is from the break-even point, the higher its level financial stability, competitiveness and profitability.

Let's look at an example of what happens to the break-even point when variable costs increase. The table below shows an example of changes in all indicators of income and costs of an enterprise.
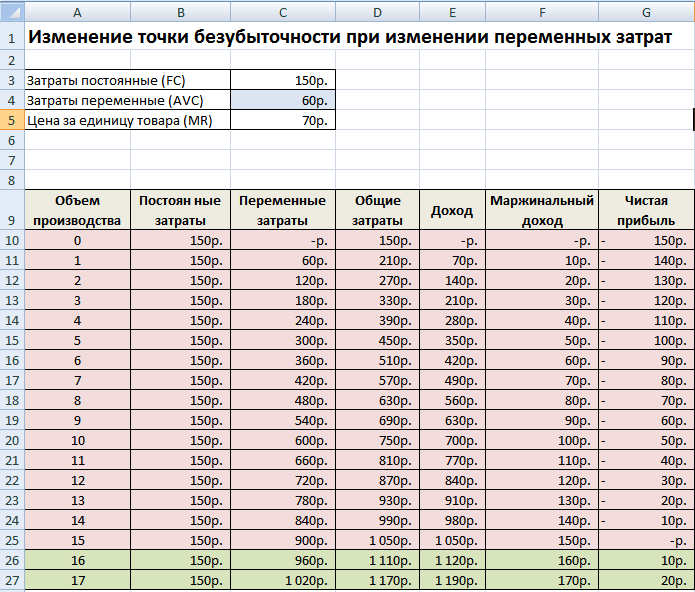
As variable costs increase, the break-even point shifts. The figure below shows a graph for achieving the break-even point in a situation where the variable costs of producing one unit of steel are not 50 rubles, but 60 rubles. As we can see, the break-even point became equal to 16 units of sales/sales or 960 rubles. income.

This model usually operates linear dependencies between production volume and income/costs. In real practice, dependencies are often nonlinear. This arises due to the fact that production/sales volume is influenced by: technology, seasonality of demand, influence of competitors, macroeconomic indicators, taxes, subsidies, economies of scale, etc. To ensure the accuracy of the model, it should be used in the short term for products with stable demand (consumption).
Summary
In this article, we examined various aspects of variable costs/costs of an enterprise, what forms them, what types of them exist, how changes in variable costs and changes in the break-even point are related. Variable costs are the most important indicator enterprises in management accounting, to create planned tasks for departments and managers to find ways to reduce their weight in total costs. To reduce variable costs, production specialization can be increased; expand the range of products using the same production facilities; increase the share of scientific and production developments to improve efficiency and quality of output.