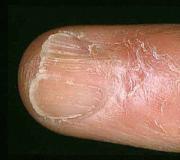
Atrophic changes in the nails. Causes of nail dystrophy and treatment methods
Diseases of the nails, in which their shape and size change, always cause great discomfort in a person and significantly reduce the quality of his life. Nails are a mirror reflecting the state of human health, and are often the first to indicate serious diseases of the body. Half of all cases of diseases is. At different stages of the development of this disease, changes in the nails are expressed in one form or another and often have a great similarity with a number of other diseases. Nails are often affected in lichen planus, psoriasis, and eczema.
Diseases of the nails in some common diseases
Fungal infection (onychomycosis)
With onychomycosis, the color changes, shine is lost, stripes and spots appear, the thickness of the nail plates increases. Over time, the nails become deformed, crumble, break down, or break away from the nail bed.
Rice. 1. The photo shows onychomycosis.
Lichen planus
Thinning of the nail plates, discoloration, delamination at the free edge, separation from the nail bed and damage to the nail folds are the main signs of lichen planus. Nails are reduced in size. Often cracks and ribbing appear on their surface. The causes of lichen planus have not yet been established. Many factors influence the development of the pathological process.

Rice. 2. In the photo, lichen planus.
Psoriasis
The causes of psoriasis have not yet been established. The disease is considered multifactorial. Undoubtedly, changes in the immune system play a large role in the development of the disease. Nail plates in psoriasis change long before the appearance of the main manifestations of the disease - psoriatic plaques on the skin. The more the matrix is involved in the pathological process, the more pronounced.
The main manifestations of psoriatic lesions in primary psoriasis: punctate depressions and pitting, separation from the nail bed, the appearance of smoky lines, increasing dryness of the nails, their fragility, the development of subungual keratosis.
In the secondary form of the disease, the nail plates change shape, scales, deep furrows appear on their surface, color changes, delamination and peeling are often noted.

Rice. 3. In the photo, nails with psoriasis.
Eczema
Eczema, like lichen planus and psoriasis, is a multifactorial disease. The nail plate during the disease changes its shape and exfoliates. Its surface is dull and rough, striated with transverse furrows. The degree of damage to the nail matrix affects the thickness of the nail itself. Frequent inflammation leads to the fact that the nail skin disappears, cracks and wounds appear.

Rice. 4. The photo shows eczema.
Changes in the shape, size and appearance of nails
Fragile nails, crumbling and brittle
Brittle, crumbling, and brittle nails are more likely to result from exposure to chemicals, water, and nail polish. They appear when the thyroid gland malfunctions. Old age is a sign of aging. The chronic course of psoriasis also leads to fragility and crumbling. Sometimes the disease is congenital.

Rice. 5. Nail diseases - onychomycosis and psoriasis.
Rough and flaky nails (trachnonychia)
Trachnonychia is most commonly seen in eczema, psoriatic lesions, neurodermatitis, and lichen planus. Such nails look dry, dull, flaky, sometimes with punctate impressions. The free edge is serrated, with a large number of cracks.

Rice. 6. In the photo of nail disease - psoriasis and eczema.
Brittle, split, and flaky nails (onychorrhexis and onychoshisis)
Splitting of the nail plates and fragility can be in the longitudinal (onychorrhexis) and transverse (onychoshisis) directions.
A common cause of this pathology is the permanent injuries that occur in musicians when playing stringed instruments and undergoing cosmetic procedures (manicure). The cause of splitting can be eczema and red lichen. Lamellar splitting is most often a congenital pathology. Onychorrhexis is most often a sign of aging.

Rice. 7. In the photo, splitting of nails in the transverse (onychoshisis) and longitudinal direction (onychorrhexis).
Longitudinal furrows
This pathology is often found in people in old age. The cause of the appearance of longitudinal furrows can be lichen planus, stress and metabolic disorders. Longitudinal furrows are found in perfectly healthy people. Each groove and ridge corresponds to protrusions located on the lower surface of the nail plate.

Rice. 8. The photo shows longitudinal furrows.
Longitudinal canal dystrophy
This type of change affects the nail plates of the thumbs. The phenomenon is characterized by the appearance of a groove (wide channel) more often in the center, less often closer to the outer edge of the nail plate. Often furrows appear after injury and disorders of the autonomic nervous system. The familial nature of the pathology is noted.

Rice. 9. The photo shows longitudinal channel-like dystrophy.
Transverse furrows
Transverse furrows are found in severe somatic diseases and exposure to a number of environmental factors. The deeper the groove, the more affected the nail matrix. Furrows often appear with a number of skin diseases, myocardial infarction, after chemotherapy, Raynaud's disease and exposure to low temperatures.

Rice. 10. In the photo there are transverse furrows (Beau-Reilly furrows).
Lateral lesion
The cause of the lateral lesion is most often a fungal infection and subungual fibromas.

Rice. 11. In the photo of nail diseases, in which there is a lateral lesion of the nail plates - onychomycosis and subungual fibromas.
cracks
Cracks always appear on healthy nail plates suddenly. The phenomenon is associated with the use of significant efforts during the processing procedure (manicure) with sharp instruments.

Rice. 12. The photo shows a cracked nail.
Thickening of nails
The most common cause of thickened nails is fungus and psoriasis. A little less often, pathology is detected with eczema, warts of the nail bed and lichen planus.

Rice. 13. In the photo of nail diseases, in which their significant thickening is noted - onychomycosis and psoriasis.
Ingrown (pincer) nail
The nail plates become pincer-shaped when their edges grow into the tissues of the nail fold, which becomes inflamed and covered with bloody crusts. The damaged surface is easily vulnerable and often bleeds. Growing granulations - "wild meat". Pus is constantly released. There is a heavy smell near the patient. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, due to which the patient begins to limp. The disease is most often recorded in young people.
The main cause of the disease is a hereditary factor, when there is a pronounced longitudinal curvature of the nail plate. Its growth takes on an oblique direction. The nail fold itself is significantly enlarged, and the nail bed is narrow.
Contributes to the disease wearing narrow shoes, improper cutting of nails, a change in the direction of growth of the big toe and injury. The disease is often recorded in persons of certain professions - ballerinas, dancers, basketball players, boxers and football players.

Rice. 14. But the photo is an ingrown nail (pincer). The roller is inflamed, covered with bloody crusts and bleeds. An increase in granulation (“wild meat”) is visible.
Claw nails (onychogryphosis)
Thickening and curvature of the nail plates occurs with injuries, wearing uncomfortable shoes, frostbite, circulatory disorders in the lower extremities and in senile people.
Often the disease is congenital in nature, when the cause of onychogryphosis is a malnutrition of the tissues of the nail bed. One or all nails are affected. They have a stony density and longitudinal furrows of yellow-brown or brown color. Sometimes their length reaches 3 - 3.5 cm. They can twist, resembling a ram's horn.

Rice. 15. In the photo, claw-like nails (onychogryphosis).
Partial detachment of nails (onycholysis)
With onycholysis, the nail plates separate from the nail bed. Fungal infection (rubromycosis) and psoriasis are the main causes of this pathology.
Thyrotoxicosis, severe intoxication, trauma and eczema also sometimes cause nail detachment. The separation begins from the side of the free edge, which acquires a white color.

Rice. 16. The photo shows a partial separation of the nail plates on the hands with rubromycosis.

Rice. 17. In the photo of nail disease - fungus and psoriasis.
Complete separation (onychomadesis)
Complete separation of the nail plate begins at the proximal edge. The process develops very quickly and is mainly recorded on the thumbs of the hands and feet. The reason for separation of the nail plate is not clear today, but it is known that the function of the matrix is significantly impaired during separation.
Sometimes the separation is preceded by trauma, sometimes by a manicure, using sharp instruments. The cause of detachment can be a fungus, psoriasis, sarcoidosis and eczema. A similar pathology is noted with a congenital disease - epidermolysis.

Rice. 18. In the photo, the complete separation of the nail plates: on the left with psoriasis, on the right with trauma.
Flat nails (platonychia)
Platonychia most often represents a congenital anomaly. Diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver and psoriasis lead to the appearance of this pathology during life. Changes always affect all nail plates.

Rice. 19. In the photo, platonychia.
Spoon nails (koilonychia)
Koilonychia is often a symptom of iron deficiency anemia. The shape of the nail plates changes with trauma, prolonged exposure to acids and alkalis, with Addison's disease, fungal infection, psoriasis, Raynaud's disease and lupus erythematosus. The family nature of this type of pathology is noted.

Rice. 20. The photo shows koilonychia.
Pinholes and dents
Pinpoint depressions and dents primarily indicate the manifestation of psoriasis and often appear long before the main symptoms of the disease. A little less often, such changes are recorded with eczema. Sometimes punctate depressions are found in perfectly healthy people.

Rice. 21. Damage to the nails in psoriasis - dotted depressions.

Rice. 22. In the photo, nail damage in psoriasis is punctate indentations.
Nail injury
Injuries to the nail plates often result in a significant cosmetic defect - deformation, destruction and hemorrhage. Bacterial endocarditis and rheumatoid arthritis can sometimes cause hemorrhages at the base of the nail.

Rice. 23. The photo shows a nail injury.
Hippocratic nails ("drum fingers")
The nails, together with the phalanges of the fingers, become domed and increase significantly in size, resembling watch glasses. Most often, this pathology occurs in patients with chronic lung diseases - tuberculosis, emphysema, neoplasms in the lungs, etc. In some patients, "drum fingers" are found in diseases of the cardiovascular system and leukemia. Often this pathology is familial.

Rice. 24. In the photo, the nails are “drumsticks”.
Absence of nail plates (anonychia)
Lichen planus, pemphigus, congenital epidermolysis bullosa are diseases in which anonychia is noted. Often the disease is familial and is a congenital pathology.

Rice. 25. In the photo, the complete absence of nail plates (anonychia).
Small nails (micronychia)
Small nails on the hands and feet and hands are a congenital pathology. The habit of biting nails, epilepsy, scleroderma, trophoneurosis are the main causes of acquired micronichia.

Rice. 26. Micronichia.

Rice. 27. In the photo, micronichia.
Pachyonychia congenita (Jadasson-Lewandowski syndrome)
Articles of the section "Fungal diseases (mycoses)"Most popularCauses of the disease:
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- nervous diseases;
- dermatosis;
How to treat onycholysis?
Causes of the disease:
- avitaminosis;
How to treat nail atrophy?

Causes of the disease
- Reduced immunity.
How to treat onychomycosis?
Causes of the disease:
- Duhring's disease;
- psoriasis;
- dermatosis;
- fungal infections;
- syphilis;
- pemphigus.
How to treat paronychia?
Pigmentation on nails

- kidney failure;
Nail atrophy is one of the diseases of the nail, which is characterized by various types of deformation, from changes in the thickness of the nail to its structure. They are congenital (more often) and then associated with endocrine system disorders, or acquired consequences of certain dermatoses (lichen planus, psoriasis), which caused damage to the nail matrix.
Grooves, thimble-like or punctate surface, splitting and fragility of the edges may be due to vitamin deficiency. Trophic changes also occur with trauma (such are ingrown nails from too tight shoes), as well as with inflammation of the nail roller (panaritium). The appearance of white dots, transverse and longitudinal stripes on the nail plate is the result of an infection that has penetrated through an unsuccessfully removed (bitten) burr.
Symptoms
In most cases, acquired atrophy can affect all parts of one or more fingers. Affected nails are usually gray-white in color, their surface is dull, with flaws. The nail at the same time has a smaller size, it is thinner than healthy nails. The substance of the nail is soft, looks like a thickened membrane. The surface of the nail plate is rough, with longitudinal cracks, it looks like it has been worn off by worms.
Treatment:
Before prescribing therapy, patients should be carefully examined, paying special attention to age, the state of the nervous and endocrine systems, and the possibility of systematic traumatization of the nails. Treatment is prescribed depending on the underlying disease. In all cases, vitamins (especially A), preparations containing calcium, iron, zinc are shown.
Showing yeast, small doses of thyroidin, dieting. Locally - fatty creams, oils with corticosteroids. The rate of nail regrowth and the change in their properties towards improvement is affected by 20% metronidazole ointment. First, the nail is detached using ureaplast (1-2 sessions), and then this ointment is applied daily for 1-1.5 months.
Treatment of an ingrown nail is associated with the normalization of the functioning of its growth zone. For this you need:
build up the cuticle on the nail hole (do not push it back);
suppress inflammation: henceforth, it is correct to cut off the overgrown edge of the nail - only parallel to the roller (the simplest trick is to lay a match over the edge of the nail and cut the nail exactly along it);
in the future, never wear uncomfortable shoes.
One of the reasons for contacting a dermatologist is nail onychodystrophy - a disease in which the appearance and structure of the plates changes.
Fragility, increased delamination, distorted nail color worsen the condition of the hands and cause discomfort to a person. Neglect of the problem is dangerous with the destruction of the matrix and the complete loss of nails.







Video:
Trays
Compress
- alum - 5 g;
- glycerin - 1 tbsp. l.;
- warm water - 70 ml.
What rub sore nails
Pathological processes on the nails, unfortunately, are not uncommon. One of the diseases of the nail plates is dystrophy (onychodystrophy). Most often, dystrophy occurs on the big toe. The disease is characterized by deformation and discoloration of the nail plate.
Sources of dystrophy
Onychodystrophy on the big toe can develop for various reasons. They may be hereditary or acquired. Hereditary dystrophy is more difficult to treat, in most cases the patient relapses.
You can get rid of the pathology if the causes of the disease are as follows:
- beriberi and ecology: and the negative impact of the environment;
- trauma: damage to the nail plate or bruised toe;
- infectious diseases: fungus, psoriasis and eczema;
- general exhaustion of the body: stress, weakened immunity, poor sleep, etc.;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
The plates of the big toe can manifest themselves in different ways. Symptoms depend on the causes that provoked the disease.
Symptoms
Signs of such a toenail problem as onychodystrophy appear gradually. In the absence of an impact on dystrophy, the symptoms begin to progress, and the condition of the nail plate on the big toe worsens.
Depending on the nature of the symptoms, the disease has several types. Most often, the following forms of the disease are diagnosed on the toenails:

- onycholysis: there is a departure of the plate from the bed;
- onychoshisis: cracking and delamination of the nail across from the edge to the bed;
- furrows Bo: the appearance of transverse furrows;
- hapalochinia: softening and loosening;
- onychorrhexis: thinning and soreness;
- trachnonchinia: stratification and change in structure;
- median channel-shaped: the formation of a horizontal groove throughout the plate.
Under the influence of various negative factors, one or another form of dystrophy can progress in a patient.
It is very important to pay attention to the signs of a pathological condition in time and seek medical help.
Nail dystrophy in children
Onychodystrophy can also occur in children. The most common causes of childhood dystrophy are beriberi, trauma, and fungal infection. Symptoms of the pathological process in children in most cases are mild.
Children are diagnosed with onychoshisis, hapalochinia, Bo's furrows and trachnonchinia. Serious big toe in children is extremely rare. At the same time, the childhood form of the disease is treated quite simply.
The use of medicines is necessary only when tissues are damaged by a fungus, in other cases it is recommended to strengthen immunity by taking vitamins and good nutrition. If the pathological process in children develops as a result of an injury, then in most cases the condition of the plate is restored after the growth of a healthy nail.

In the case when childhood dystrophy is observed, it is necessary to visit a specialist who will identify the cause and, if necessary, prescribe treatment or give certain recommendations.
Such a disease should not be treated without prior diagnosis.
Treatment of pathology in adults
To get rid of the thinning and deformation of toenails can be different methods. The main treatment should be medication. In the form of additional therapy, folk remedies are used. In advanced cases, the patient may require surgery or laser treatment.
Medical therapy
Treatment of dystrophy begins with determining the cause of the disease. To cope with the pathological process is possible only by eliminating the cause. Depending on the clinical picture, the specialist prescribes treatment according to a certain scheme. Treatment is carried out with medications that have a directed action:
- beriberi: taking vitamin complexes, proper nutrition and getting rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.);
- trauma: drugs that increase tissue regeneration and reduce the effects of bruises;
- infections: antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs (prescribed individually);
- depletion of the body: antidepressants, sedatives, vitamins, etc.;
- problems with the endocrine system: groups of drugs are taken in a complex and are selected by a specialist depending on the type of pathology.

Treatment of dystrophy with medicines should be carried out only after visiting a doctor and in accordance with his instructions. Most drugs have contraindications, so self-treatment can be dangerous.
Folk remedies
Onychodystrophy of the big toe nail can be successfully treated with traditional medicine, but only at the first stage. In the future, complex therapy should be carried out. For treatment, agents with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties are used. Also, the products and plants used should enrich the tissues and the whole body with useful microelements.
- Iodine. You should lubricate problem areas with iodine several times a day. Do these procedures for ten days. Five days later, the course is repeated.
- Propolis. It is necessary to lubricate the injured places with propolis at night for three days.
- Salt solution. The legs are kept in saline for twenty minutes. To prepare the solution, you need to mix 4 tbsp. salt in a liter of water. After the bath, lubricate the nail with beeswax.
It is possible to prevent the appearance of onychodystrophy. To do this, preventive measures should be followed, which include proper nutrition, regular foot care and hygiene.
Nail dystrophy is a pathological process, the characteristic manifestations of which are a modification of the shape and structure of the plates or periungual ridges. The disease has a non-fungal origin, is diagnosed on average in 3-4% of the population. A variety of infections, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the circulatory system and heart can contribute to the development of dystrophy on the nails.
The main causes of the onset of the disease in adults
Dystrophy of the nail plate is a problem that can affect every person. Residents of cities are most affected by it. The formation of white spots, the fragility of nails, their delamination are symptoms of dystrophy, which has a large number of root causes and varieties. Localization of the disease can be observed on the arms and legs. The most common causes of nail dystrophy in adults include:
- poor environmental background, manifested in air pollution, poor quality of drinking water;
- avitaminosis - lack of vitamins due to malnutrition;
- injuries on the fingers, toes;
- eczema or psoriasis;
- diseases of a fungal nature that affect the horny tissue of the nails;
- weak immunity that occurs against the background of constant stress, inadequate rest, prolonged infectious diseases;
- disorders of the endocrine system;
- cardiovascular pathologies leading to circulatory disorders and, as a result, weakening the nail plate.
Why does nail dystrophy develop in children

The causes of such nail damage in adults and children are almost the same. Often this condition is due to low immunity, frequent chemical, traumatic effects on the nails. The appearance of longitudinal and transverse grooves on the nails may indicate a congenital pathology, skin diseases. The following causes of the formation of this disease in children are distinguished:
- improper care;
- trauma;
- malnutrition;
- transferred infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- psoriasis, dermatitis and eczema contribute to the formation of a secondary form of dystrophy.
The most common types of dystrophy of the nail plate

This pathology can be presented in various forms, each of which has its own characteristic features, and also requires a certain treatment. Only an experienced specialist can recognize the type of nail dystrophy. Based on this, he will prescribe an effective therapy. There are several types of pathology:
- median canal;
- furrow Bo;
- hapalochinia;
- onychorrhexis.
Median canal dystrophy

This type of dystrophy is characterized by the presence of a wavy surface on the nails, a transverse arcuate depression that looks like a groove or groove, the width of which is up to 4 mm. The plates resemble a forked washboard. Small erosion, peeling, scratching can form near the rollers. Such dystrophy is diagnosed in people experiencing permanent nervous and mental disorders. Therapeutic measures include psychological conversations, the use of sedative herbal medicines, tranquilizers.
Furrows Bo

This type of dystrophy is more common than others. With such a disease, a transverse groove forms on the nail. It crosses the surface of the nail plate from one lateral ridge to another. The Bo furrow is characterized by the presence of a slightly elevated ridge along one edge. Common causes of such a pathology are an inflammatory process, trauma to the nail roller, or skin damage during a manicure. The damaged area can be divided into two halves. As a result, contact between the free part of the nail bed and the plate is lost, but the growth of the nail continues.
Gapalonychia

This type of dystrophy is characterized by such manifestations as softening of the nail plate, thinness, layering and brittleness. The main reasons for the formation of hapalonychia are pathological processes in the internal organs. The treatment of such a disease is aimed, first of all, at stopping the cause, and then at eliminating the external signs that have arisen.
Onychorrhexis

The pathological process called "onychorrhexis" ranks second in the ranking of the most common diseases of the nail plate. It is characterized by the formation of a crack in the direction longitudinal from the free edge. The result of this process is the delamination of the nail, its fragility. In addition, air accumulates under the nail. It also serves as a frequent cause of the formation of onychorrhexis. The main factors in the development of such a pathology include:
- eczema;
- lichen;
- varicose veins;
- endocrine disorders;
- avitaminosis;
- cholelithiasis;
- fungal diseases.
How to treat nail dystrophy at home

Treatment of nail dystrophy on the hands and feet should be agreed with the doctor. He must take into account all the characteristics of the patient's body. The therapy of such a disease always has an integrated approach and is aimed at determining the cause of the pathology and its relief, regeneration of the trophism of the nail and tissues around it. It includes the use of ointments, drugs, alternative recipes or surgery.
Medical treatment

Therapy of dystrophic changes in the nail plates with the help of drugs involves the use of drugs of two groups: sedatives and drugs that block the sympathetic nervous system. Only she sends impulses to the sweat glands. Sweating plays a major role in the thermoregulation of the body. With frequent sweating, local swelling of the skin occurs, for example, around the fingers. The result of this process can be dystrophy of the nail plate.
Therapy of such a pathology should take place directly under the guidance of a doctor, because many of the available drugs have contraindications and side effects. The following medications will help eliminate all manifestations of dystrophy:
- Valerian, motherwort can be prescribed as a medicine, herbal preparations or homeopathic preparations.
- With the initial development of the disease, antiperspirants are used (drugs that are actively used to treat conditions associated with anxiety, bad mood, apathy, emotional overstrain, melancholy). Their action is aimed at narrowing the tubules through which sweat penetrates the skin. The result of such treatment of nails on the hands and feet is the normalization of sweating.
- Preparations of angioprotective (protecting blood vessels) action. They help to improve microcirculation in the tissues of the hands and feet. Effective drugs of this action are Detralex, Endotelon.

- Mineral and vitamin complexes to increase the content of vitamins B, A, E, sulfur, selenium, calcium in the body.
Folk remedies
Treatment of nail dystrophy may include alternative methods. They are used primarily as adjunctive therapy. Thanks to the local use of traditional medicine, it is possible to restore damaged nails in a short time, normalize the nutrition of the periungual tissues. Treatment of dystrophy of the nail plates with folk remedies includes the following recipes:

- Iodine. Treat nails with 5% tincture of iodine 2 times a day. The duration of therapy is 10 days, then a break for 2 days, and then repeat the course again.
- Propolis. Use 20% tincture for compresses at night. During application, avoid getting the product on the skin, otherwise it will cause a burn. The number of procedures is 2-3.
- Baths. They have a good effect on the deformation of nails. For the preparation of baths, sea salt is used. A tablespoon of the substance is diluted in a glass of warm water, and then poured into a container and dipped into the solution for 10-15 minutes. After the procedure, they must be wiped with a soft towel and natural wax rubbed into the skin.
Photo of nail dystrophy on the hands and feet
Dystrophy of the nail plate in the photo below is a pathology that not only disrupts the growth and shape of the nails, but also spoils their appearance. Only the use of complex diagnostic and therapeutic measures will help restore the former beauty of the nails. But there are cases when the only way to eliminate the pathology is surgery. The following photos will help to better imagine the forms of this disease.
Source: dvah.ru
Signs of atrophy
- Nail plates are deformed;
- Nails take on a gray tint;
- The thickness of the nail decreases, its crumbling is possible;
- The plate becomes soft;
- The abundance of flaws and inclusions on the nails;
- The nail plate moves away from the bed;
Treatment of nail atrophy
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner before the disease begins to progress. In the treatment of nail atrophy, age, the state of the endocrine system, and possible causes of nail injury are taken into account. The method of treatment is prescribed depending on the disease, however, in all cases, vitamins (most often vitamin A) and minerals (iron, potassium, zinc) are indicated.
In the treatment of atrophy, creams, oils with corticosteroids are often prescribed. A proper diet is also required.
With an ingrown nail, it is required to normalize the functioning of its growth zone, for this, the skin is grown next to the nail hole, the free edge of the nail is cut parallel to the roller.
Nail atrophy can be treated at home. To do this, you need to drink a course of vitamins and minerals and prepare a bath with sea salt or propolis ointment.
Baths with sea salt
To do this, dissolve a small amount of sea salt in a bowl of warm water, you can also add a few drops of iodine to the bowl. Dip your hands in a bowl for 15 minutes so that your nails are completely in the water. After the bath, dry your hands with a napkin, but do not rinse them with running water. You can also use an antifungal cream.
Ointment from propolis
Stir the pounded propolis with alcohol, in an amount of 1: 1. Then steam your hands and apply the resulting mixture to the problem areas of the nails. At night, you should spread a larger problem area and wrap your finger with a bandage. Change this bandage daily.
Remember that in the treatment of diseases of the toenails it is necessary to avoid wearing uncomfortable shoes.
Source: nails-info.ru
Acquired and congenital atrophy.
Congenital atrophy of the nail develops most often in connection with a violation of the functioning of the endocrine system.
Acquired atrophy is a consequence:
- various skin diseases (psoriasis, lichen), if they have affected the nail matrix
- vitamin deficiency (this manifests itself externally in the form of dots on the surface of the nail, grooves, fragility or splitting of nails)
- injury or inflammation (especially if you wear tight shoes)
- with careless removal of the cuticle if an infection has got (white dots or stripes appear on the nail plate)
Treatment of nail atrophy.
Treatment of atrophy of the nails of the hands. It is necessary to consult a doctor. This usually takes into account the age of the patient, his state of the endocrine system, as well as the presence of nail injuries. The method of treatment depends on the underlying diagnosed disease. It is possible to prescribe vitamins (most often it is vitamin A), as well as various useful minerals, such as calcium, iron or zinc. Sometimes various ointments are prescribed with special recipes for use, as well as compliance with the necessary diet.
If the nail has grown, then its treatment is based on the goal of restoring the normal activity of the nail growth zone and is treated as follows:
- skin grows near the nail hole
- the free edge of the nail is cut off only parallel to the roller, not at the very root, this helps to suppress inflammation of the nail
- it is recommended to avoid uncomfortable shoes
And it’s better to just never face such diseases, taking care of your nails. Be healthy and don't get sick!
To cheer up a little, already loved themed mix:
“Nails - not teeth, break off - grow back.“
Source: Moi-Manikur.ru
Why does nail dystrophy develop?
Signs of dystrophy can be observed on the plates of the upper and lower extremities.
The reasons for the defeat are countless, but the most common of them are:
- finger injuries leading to detachment of the nail;
- vitamin deficiency, causing brittleness and delamination of the plate;
- infection, in which the horny tissue is most often affected on the legs;
- endocrine disorders and disorders in the circulatory system;
- polluted ecology - the use of poor-quality water and living in industrial regions affects the general well-being of a person and the health of nails;
- poor immunity. The protective functions of the body are affected by protracted infectious pathologies, lack of rest, constant stress and anxiety. The body weakens and picks up any sores that affect the condition of the nails and hair.
Often, onychodystrophy of the nails develops against the background of skin diseases - eczema, psoriasis, and due to mechanical damage to the nail itself, the roller or bed.
In women, nail damage is promoted by their extension and coating with poor quality decorative varnishes. In nervous people, the disease develops due to the habit of picking and biting nails, as well as biting burrs.
Common types of deformations
What symptoms will manifest onychodystrophy, depends on its variety.

- Gapalonychia, in which the plates become brittle and brittle due to excessive softening and thinning.
- Onychoshisis. This form of the disease causes cracking and splitting of the nails. Cracks form across the growth of the plate, and delamination of the structure is observed along the edge.
- Onycholysis is the most unpleasant form that develops under the influence of various factors and is expressed by the gradual detachment of the nail.
- Onychogryphosis, or "bird's claw". In the process of growth and deformation, the plate becomes similar to the claw of a bird of prey. Occasionally, it grows into the skin of the finger or takes a spiral shape. Pathology is painful. The color of the plate is grayish or brownish.
- Trachnonichia. The characteristic features of this type of deformation are the dullness and roughness of the plates. Scales and dotted pits speak of damage to nails.
- Furrows Bo. Transverse recesses occupy no more than 1 mm. Pathology does not cause unpleasant sensations, the shade of the nail tissue does not change. It appears due to injury to the nails and during exacerbation.
- Median dystrophy is similar to the previous state, only longitudinal grooves are formed.
Dystrophy of nails in the likeness of watch glasses occurs only on the hands and in people suffering from chronic broncho-pulmonary diseases, heart pathologies and disorders of the endocrine and digestive systems. Hypertrophied fingers (hippocratic nails) resemble drumsticks (photo at the beginning of the article).
External signs of various forms of onychodystrophy are shown in the photo.






Do not let the disease take its course and start treatment in a timely manner.
Video:
How to treat deformed nails?
Most congenital and some types of acquired onychodystrophies cannot be treated. If the disease has developed as a secondary pathology, its manifestations disappear during the treatment of the underlying disease.
Treatment of nail deformities is always carried out in a complex and taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism. The tactics are aimed at eliminating the harmful factor and restoring the nutrition of the nails along with the adjacent tissues.
Therapeutic regimens against onychodystrophy are based on several activities:
Physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of nails are used such: iontophoresis, phonophoresis with vitamins A and E, diathermy. One course is designed for 10-15 procedures with a mandatory break for 1-2 months.
To improve the nutrition of the nail areas of the fingers, patients are prescribed vitamin-mineral complexes, preparations with amino acids and unsaturated fatty acids. They contribute to the proper formation of the nail. The course of therapy necessarily includes restorative, sedative and immunomodulatory medicines and means to restore the emotional background.
Prevention of nail onychodystrophy is reduced to the exclusion of the possibility of damage to the plates and the formation of subungual hematomas and the preservation of the integrity of the matrix. Experts recommend taking vitamins regularly and eating only wholesome foods.
Improvement of nails without drugs
The problem of fragile exfoliating nails can be solved with the help of traditional medicine recipes. Baths, compresses, rubbing, healing thimbles - all these methods strengthen nails and bring recovery closer.
Let's consider how, with onycholysis disease, patients can treat with folk remedies at home.
Trays
Compress
A therapeutic preparation for applying compresses is prepared from the following components:
- alum - 5 g;
- glycerin - 1 tbsp. l.;
- warm water - 70 ml.
A piece of gauze is moistened with the product and a compress is wrapped around the phalanges with nails. Remove the bandage after 30 minutes.
What rub sore nails
The simplest remedies for the treatment of various types of onychodystrophy are iodine and cranberry and currant juices. Rubbing substances into the nails for a week gives good results. Iodine treatment is recommended to be carried out at night so that the natural color of the plates is restored before morning.
Another recipe for rubbing is to steam 1 tbsp. l. olive oil and add 5 drops of iodine to the product. The procedure is performed before going to bed by rubbing nails and adjacent tissues.
According to statistics, only every tenth person has healthy nails. The remaining nine notice a change in the shape, thickness or structure of the nail plates, their departure from the nail bed.
One of the conditions in which similar symptoms are observed is nail atrophy. At the same time, the nail plate looks different: it may become too thin, stripes or pinpoint impressions may appear on it, and its color may change. But there are some common features that allow you to make a diagnosis.
The disease develops due to various reasons, including due to congenital malformations or fungal infection. It is possible to cure nail atrophy at home, but for this you need to direct efforts to eliminate the disease that caused it.
Causes and classification of the disease
Depending on the cause, nail atrophy can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital
Occur in one of two situations. The first is when a defective gene is transmitted from one of the parents. As, for example, in Turner-Kizer syndrome, in which, along with nail atrophy, there are multiple defects in the skin, bones (underdeveloped patella, enlarged frontal tubercles, dislocation of the radius bones, and others), muscles (they are underdeveloped on one or several different parts of the body).
The second is in which congenital nail atrophy is formed in children if the pregnant woman suffers from some kind of chronic disease (mainly endocrine pathologies), or suffered an acute infectious pathology in the 1-2 trimester.
Acquired
They occur in both children and adults. Their main reasons are:
- skin diseases:,;
- deficiency of vitamins A (it should contribute to the normal moisture of the nail, prevent its delamination), C (prevents overdrying of the plates), E (ensures their growth) or B (responsible for growth and strengthening);
- deficiency of trace elements such as sulfur, calcium, chromium, silicon, phosphorus, iron, selenium;
- injuries of the nail plate (on the legs this comes from wearing tight shoes);
- inflammation of the nail, which can develop as a result of a fungal infection (), as well as infection with pyogenic bacteria that have entered through an unsuccessfully removed barb or injury to the periungual skin;
- toxic components of varnishes or building materials;
- damage to the peripheral nerves that go to the fingers (polyneuropathy). It develops with diabetes mellitus, constant alcohol consumption, after some past viral infections, as well as with diseases that are autoimmune in nature, which are called demyelinating (the outer sheath of the nerve trunks, myelin, is destroyed);
- intoxication: alcohol, methyl alcohol, heavy metals;
- the influence of certain drugs: based on isotretinoin (it is used to treat acne), antibiotics (especially anti-tuberculosis) Tetracycline, Isoniazid, Doxorubicin. Can cause atrophy and anesthetic drug "Indomethacin";
- diseases of the digestive system, in which not only the necessary substances are not absorbed, but harmful substances formed as a result of the disease itself are released into the blood.

Nail psoriasis
What underlies nail atrophy
The nail plate is a protein keratin: the same that makes up the hair and is found in the skin. It is denser because it contains more sulfur atoms in an amino acid called cysteine. Cysteine forms many bridges between its own molecules and keratin molecules.
The nail is formed from the matrix. This is a cluster of cells located closer to the joint between the last and middle phalanges of the finger. The matrix is completely covered with skin, and only a small part of it we see as a white area of a crescent shape. Several layers of cells are formed from the matrix. One of them (prickly) gives rise to the nail plate.
In order for the matrix to exist normally, it must receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This function is carried out by a developed network of blood vessels. The activity of these capillaries is regulated by nerve endings. Everything that affects vascular tone and the work of nerve endings in this area worsens the work of the matrix. And if the growth zone cannot function normally, it is unable to synthesize a normal nail plate.
If the damaging effect on the matrix is stopped in time, the nail will grow by 0.1 mm per day. Full recovery will take at least 170 days.

Symptoms of the disease
You can understand that nail atrophy is taking place here by the following symptoms:
- nail plates become thinner;
- the surface of the nail becomes gray-white or grayish, loses its characteristic luster;
- the affected nail plates change their shape: they can become concave like a spoon, flat or pterygoid;
- grooves or small crater-shaped depressions appear on the surface, arranged in random order or, on the contrary, in longitudinal rows;
- the edges may be split or too brittle;
- damaged by injury or too tight shoes, the nail plate often grows into the lateral skin folds. The opposite situation can also be observed: atrophy of the nail and its separation from the bed.
In part, the appearance of the plate will depend on the cause that caused its atrophy. So, if the basis is infection with a fungal infection, the nail acquires a yellowish tint, its thickness in some areas becomes larger, in others - less. Detachment of a thinned plate from the skin under it is characteristic of injuries, as a result of which a hematoma appeared under it, onychomycosis, as well as diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous or endocrine system.

Damage to the nail plate with a fungal infection
Pinpoint atrophy of the nails indicates that the damage to the matrix was due to a lack of one of the above vitamins, psoriasis, or lichen planus. If the points on closer inspection have three teeth, this speaks in favor of the Turner-Kizer syndrome (in this case, you need to look for pathology from the bone and muscle systems).

Point atrophy
How is the diagnosis made?
A dermatologist can make a diagnosis of atrophy only on the basis of a visual examination. But in order for the treatment of nail atrophy to be correct, the cause of this condition must be established. For this, microscopic and bacteriological examination of scrapings from damaged areas of the nail plates, as well as the contents that were under them, is performed. It is very important to carry out such a diagnosis as soon as possible. So, in the presence of a fungal infection, it can spread to neighboring nail plates.
Treatment
The answer to the question of how to treat nail atrophy comes from the causes of the disease. So, with a fungal infection, the main method of therapy will be treatment with antifungal drugs. Whereas in case of systemic diseases that disrupt local blood circulation, it is mandatory to take drugs that reduce the activity of the immune system.
home therapy
Treatment at home will depend on the condition of the nail plate. If it is prone to flaking from the free edge, or it is known that the disease is caused by a fungus, mechanical removal of the lagging part with scissors or wire cutters is used. Further, the nail and the skin under it are subject to the mandatory application of antifungal ointments or creams: Ketoconazole, Lamisil or others.
If the nail plate exfoliates and thickens locally, keratolytic patches based on salicylic acid (Salipod) or urea (Ureaplast, Onychoplast) are applied. The plaster mass is applied to the nail after the nail file or scalpel has carefully scraped off the upper shiny layer of the plate. The same treatment is indicated if the atrophy is caused by a fungal infection, but there is no tendency for the nail to detach from its bed.
For most types of nail atrophy, hot baths are also indicated. They need to mix sea salt (1 tsp per glass of water), 2-3 drops of tea tree essential oil. The fingers are immersed in water until it cools completely, then they can be blotted with a napkin, but not washed under running water. Such baths are contraindicated in the development of purulent processes (felons, paronychia) of the phalanges. Just after their application, a keratolytic patch mixture is applied. Also, after them, it is optimal to massage or perform applications of warm natural wax, paraffin-ozocerite mixture or therapeutic mud on the area of the nail itself, the cuticle and side ridges.
You can also use such a folk recipe: mix pounded propolis and 70% alcohol 1: 1, insist for 3 hours, and then apply (after the bath) to the affected nails, fixing it with cling film and a bandage on top. It is best to leave this cream overnight.
Medical therapy
A doctor may prescribe such effective drugs as:
- vitamin-mineral complexes, which necessarily contain retinol, zinc, calcium and iron;
- sedatives;
- restorative means;
- polyunsaturated fatty acids.
If necessary, ointments with corticosteroid hormones or antibacterial metronidazole ointment are used.
If the atrophied plate has exfoliated by more than a third, it is completely removed on an outpatient basis. If the finger around the nail is reddened, enlarged and sore, you need to contact the surgeon: you may need to open the paronychia.
During and after treatment, be sure to avoid wearing tight shoes. If the nails on the hands have undergone pathology, then while washing dishes, as well as when working with industrial or household chemicals, you need to wear 1 or even 2 pairs of protective gloves.
Pathologies of the nail plates are called onychopathy. Most of them are diseases of fungal or viral origin. But also among them, onychodystrophy of the nails is distinguished - this is not an infectious disease, the cause of which can be dermatosis, skin infections, and so on. Treatment in women and men is to exclude the cause and normalize the nail plate.
Description
Nail onychodystrophy is a complex of changes in the nail plate, which is characterized by malfunctions of the nail apparatus. This pathology has no features (seasonal, age, gender, racial) and can overtake anyone.
Important! Nail dystrophy can be an independent disease or indicate the development of a more serious problem.
With onychodystrophy, the nail changes color, structure, density. This can be seen with the naked eye - the nail begins to "cloud", delaminate, furrows or point extrusion appear on it. With untimely treatment, onychodystrophy can lead to complete destruction of the nail.
Diagnosis occurs by removing a scraping from the lesion, a blood test for the presence of alkaline phosphatase in it.
Causes
The epidermal matrix of the nail bed provides blood supply to the nail plate, innervation and reproduction of horny cells. If the adhesion of this bed and the nail plate itself is low or for some reason not constant, onychodystrophy occurs.
The triggers of this disease can be congenital anomalies, intoxication and a number of other factors, including:
- injuries to the fingers or toes that lead to detachment of the nail plate;
- beriberi, leading to weakening of the nail;
- pathology of the endocrine nature;
- disorders of the circulatory system - thrombosis, varicose veins;
- low immunity;
- excessive exposure to the nail with chemical detergents;
- severe stress.
Symptoms and types
Onychodystrophy is conditionally divided into several types, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms and manifestations.
- Onychoshisis - manifested by cracking and delamination of the nail plate. Cracks are observed across the nail, and its peeling and foliation - along the edges.
- Onycholysis is the most painful and unpleasant form. It is expressed by a strong delamination of the nail, which is very difficult to stop.
A beautiful manicure is the key to the well-groomedness of any girl. But what if the claws are not in the best shape? In the article "" you can understand this unpleasant problem in more detail.
- Onychogryphosis - also called "bird's claw". The nail plate grows and completely deforms, becoming like the claw of a bird of prey. In advanced cases, it can grow into the skin or take a spiral shape. With all this, the color of the nail changes to grayish with a brown tint.
- Gapalonychia - nails soften and thin, becoming very brittle.
- Trachnonichia - scales and small pits form on the surface of the nail plate.
- Furrows Bo - are small (up to 1 mm) transverse indentations on the nail. Most often occurs due to injury to the plate.
Treatment
It is very important to get rid of the pathology in the early stages in order to avoid complications or complete loss of the nail. For this, it is recommended to use special medications or use simple recipes of traditional medicine.
Onychodystrophy can be very similar to nail fungus. But for the treatment of viral pathology, completely different drugs are usually used. For example, an effective remedy against this disease is "".
Medical
As a rule, various ointments and creams are used to treat all types of onychodystrophy. Among them it is worth paying attention to:
- Pencil "Peklavus" - restores the structure of the nail, its color, stimulates rapid growth. The main active ingredients are proline (amino acid) and biotin (vitamin). These components penetrate directly into the nail matrix and restore it from the inside.
- Adhesive plaster "Onychoplast" - most often used for onychomycosis. It is a keratolytic patch that allows you to get rid of a diseased nail in order to be able to heal the bed and grow a healthy plate. The composition includes lanolin, urea, paraffin, which gently soften and exfoliate the nail.
- Flexitol gel is a softening gel that is used to eliminate dryness and cracked areas on the skin (feet, elbows, knees). With onychodystrophy, it is used in combination with other drugs to soften the keratinized skin around the nail plate.
- Salicylic-zinc ointment - is an antiseptic and disinfectant that actively dries and exfoliates the stratum corneum of the nail. Salicylic acid in a small dosage has a mild antiseptic effect, and zinc has an adsorbing effect.
- Tablets "Volvit" - the main active ingredient is biotin. The drug is used for various skin diseases, nail anomalies, destruction of hair structures. Restores biotin reserves in the body, promotes the speedy regeneration of young cells.
Folk methods
Among the most effective and gentle methods of alternative medicine, the following recipes for the treatment of onychodystrophy are distinguished.
- Iodine and propolis
Lubricate affected nails with 5% iodine solution. From above, make a compress of 20% propolis tincture, tightly bandage and leave overnight. Repeat 10 days. - Tea tree oil
Wipe the nail plate with a cotton pad soaked in tea tree oil throughout the day. Do at least 7-9 such procedures per day. Repeat 5-8 days. - Aloe juice
Rinse the cut leaf of the plant thoroughly and cut it lengthwise. Divide it into small pieces and attach the inside to the affected nail. Fix with a plaster and wrap with a bandage, leave for 3-4 hours. Repeat once a day for 2 weeks.
In addition, various nail baths are actively used in the treatment of onychodystrophy.
- with gelatin
Dissolve 1 tablespoon of gelatin in a glass of warm water. Pour into a small container and dip your fingers into it for 20 minutes. Then rinse with warm water and pat dry. Repeat 1 time in 2-3 days for a month. - With apple cider vinegar
Mix vegetable oil with table apple cider vinegar in a ratio of 2: 1. Pour into a bath container, dip your fingers into it for 15 minutes. After that, wash your fingers and nails under running water with antibacterial soap. Repeat once a week 2-3 times. - With sea salt
Dissolve 2 tablespoons of sea salt (preferably fine) in a liter of hot water. Cool to 35°C and put your hands in the bath for 15-20 minutes (until the water has completely cooled). Wet hands with a soft towel, repeat 1 time in 3 days for 3-4 weeks.
Many doctors, not without reason, believe that a person’s health can be judged by the appearance of the nail plates, and diseases of the nails on the hands clearly indicate the presence of certain problems in the body. Today we will try to identify the symptoms of the most common nail diseases, as well as highlight the main methods of their treatment.

Onycholysis is a type of dystrophy of the nail plates, which leads to a violation of the bonds between the hard part and the soft tissues of the bed. In simple terms, onycholysis is a pathological detachment of the nail. Most often, this disease occurs among the representatives of the beautiful half of humanity. Onycholysis can be complete and partial - it depends on the area of the exfoliated part.
Causes of the disease:
- eczema;
- mechanical impact on the nail plate (traumatic onycholysis);
- psoriasis;
- some infectious diseases;
- nervous diseases;
- dermatosis;
- disorders of the digestive and endocrine systems;
- problems associated with the cardiovascular system;
- in some cases, the cause of onycholysis is long-term use of antibiotics.
How to treat onycholysis?
Treatment of onycholysis is reduced to the elimination of the main causes of the disease. At the same time, it is necessary to take medicines that contribute to the overall strengthening of the body. These are preparations of iron, zinc, calcium, as well as vitamins of groups B, C and A. Doctors also recommend consuming 5-7 grams of gelatin daily. The course of treatment is 2-3 months.
As local therapy, heliomycin ointment (5%), synthomycin emulsion and potassium permanganate are used. If the first two remedies are applied to damaged plates in the form of a compress, then potassium permanganate is added to hot water and used for nail baths. Simultaneously with these procedures, it is necessary to massage the affected fingers. It will speed up the healing process.
As for prevention, try to avoid injury to the nails and do not forget about the rules of personal hygiene.
Atrophy - change in the shape of the nail plates
Diseases of the nails on the hands, associated with various deformations of the growth, shape and structure of the nail plates, are not so rare. So atrophy, congenital or acquired, affects about 40% of the inhabitants of our country. The main symptom of the disease is a change in the shape of the nail. It becomes concave or, conversely, unnaturally flat.
Causes of the disease:
- avitaminosis;
- panaritium - inflammation of the nail fold;
- mechanical damage to the nail plates;
- disturbances in the work of the endocrine glands.
How to treat nail atrophy?
To ensure the correct treatment of nail atrophy, you will have to undergo an additional examination by several specialists - a neurologist, endocrinologist, dermatologist. A special diet, eating yeast, as well as multivitamins and preparations containing zinc, calcium and iron is a must. In very severe cases, corticosteroid ointments, creams and oils (fatty) are practiced.
Onychomycosis is a common fungal disease

Onychomycosis of the nails begins from the lateral or free edge of the plate. It is characterized by the appearance of yellowish and grayish spots, which increase in size and make the nail loose and brittle. Some patients also noticed that the nails began to crumble badly as a result of the disease. Onychomycosis is dangerous for its toxic effects on the immune and nervous system - the fungus decomposes the tissue of the plate and delivers the products of its own vital activity into the blood, which poison the human body.
Causes of the disease
- Dermatophyte fungus. But in order for it to penetrate the nail plate, it must be damaged (household or sports injuries, excessive filing of the nail, improper removal of the cuticle).
- Reduced immunity.
- Skin and nails steamed in hot water.
- Frequent exposure to damp environments.
- Metabolic diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and others.
How to treat onychomycosis?
The treatment of this disease promises to be complex, lengthy and rather complicated. From the patient it requires patience, self-discipline and a lot of money. In some cases, doctors resort to removing the affected plates, after which fungicidal therapy is performed on the exposed nail bed. For external use, you will need special antifungal ointments, for internal use - Nizoral (drink for at least six months).
Be prepared to thoroughly disinfect bedding and common areas, and change gloves and mittens. For the treatment of fabrics and surfaces, 1% chlorhexidine bigluconate and ordinary bleach are suitable.
Paronychia is a serious infectious disease.
Paronychia is an infectious disease that affects the nail itself or the skin at its base. This is one of the most common hand diseases that requires urgent medical treatment.
A sign of paronychia is the darkening of the nail plate, fever, severe throbbing pain, swelling of the finger and the appearance of a purulent sac in the focus of infection.
Causes of the disease:
- paronychia is caused by a skin bacterium that enters the damaged skin. The activation of this bacterium is promoted by sucking a finger, biting off nails, washing dishes with chemicals, etc.;
- chronic eczema of the hands;
- Duhring's disease;
- psoriasis;
- dermatosis;
- fungal infections;
- syphilis;
- pemphigus.
How to treat paronychia?
In the early stages, the treatment of paronychia is reduced to the implementation of therapeutic procedures - the use of disinfectant baths with a solution of potassium permanganate + antiseptic preparations. Severe forms of the disease are not complete without surgical intervention, which consists in removing the affected nail and / or opening the purulent sac.
Pigmentation on nails

Various pigment anomalies (white spots on the nails) are familiar to each of us. Their appearance is associated with a number of factors.
Causes of pigmentation on the nails:
- malnutrition and strict diets, during which the body experiences an acute deficiency of vitamins and trace elements;
- an excess of nutrients;
- problems in the work of the cardiovascular and digestive systems;
- kidney failure;
- experiencing severe nervous shocks, stress and depression;
- decreased immunity, including after childbirth;
- mechanical damage to the nail plate;
- childhood. A growing organism does not have time to assimilate incoming substances;
- fungal infection of the nails, which is accompanied by itching, discoloration of the nail and its thickening.
How to treat pigment anomalies?
Most of us think we just need to give our nails a little time. Yes, the plate will grow back, and you will be able to cut off the ugly white spots, but this will not save you from the disease itself. The first step is to get a consultation with a dermatologist and pay attention to your own diet. Foods rich in calcium, zinc and iron should appear on your table. It is also worth drinking a course of vitamin complexes. If the cause of white spots is nervous overstrain, you will have to think about taking sedatives.
Baths play an important role in the treatment of pigmented anomalies. They speed up blood flow to the hands, which allows you to saturate the nails with more nutrients. After such a bath, you can lubricate your nails with fish oil.
You can find more detailed information about the symptoms and treatments for these and many other nail diseases in the following articles.
Video on proper nail care:
The processes of dystrophy can relate to their thickness, width, shape, consistency, from which nails appear flat, pterygoid, concave (spoon-shaped). They are congenital (more often) and then associated with endocrine system disorders, or acquired consequences of certain dermatoses (lichen planus, psoriasis), which caused damage to the nail matrix. Grooves, thimble-like or punctate surface, splitting and fragility of the edges may be due to vitamin deficiency. Trophic changes also occur with trauma (such are ingrown nails from too tight shoes), as well as with inflammation of the nail roller (panaritium). The appearance of white dots, transverse and longitudinal stripes on the nail plate is the result of an infection that has penetrated through an unsuccessfully removed (bitten) burr.
Treatment.
Before prescribing therapy, patients should be carefully examined, paying special attention to age, the state of the nervous and endocrine systems, and the possibility of systematic traumatization of the nails. Treatment is prescribed depending on the underlying disease. In all cases, vitamins (especially A), preparations containing calcium, iron, zinc are shown. Showing yeast, small doses of thyroidin, dieting. Locally - fatty creams, oils with corticosteroids. The rate of nail regrowth and the change in their properties towards improvement is affected by 20% metronidazole ointment. First, the nail is detached using ureaplast (1-2 sessions), and then this ointment is applied daily for 1-1.5 months.
Treatment of an ingrown nail is associated with the normalization of the functioning of its growth zone. To do this, it is necessary: a) to build up the cuticle on the nail hole (do not move it away); b) suppress inflammation: henceforth, it is correct to cut off the regrown edge of the nail - only parallel to the roller (the simplest trick is to lay a match over the edge of the nail and cut the nail exactly along it); d) never wear uncomfortable shoes in the future.
See also:
anonychia
Congenital absence of nails belongs to a group of rare hereditary anomalies. It can be manifested by the absence of one or more (all) nails and, as a rule, is combined with other disorders of the outer layer of the skin, sweat and sebaceous glands, changes in the structure of the hair and other malformations ...
Onycholysis
A common type of nail dystrophy, in which the connection between the nail and the soft tissues of the bed is disrupted. Depending on the size of the detached part of the nail, partial and complete onycholysis is distinguished, more often in women. Its reasons are manifold. Traumatic develops as a result of mechanical, physical, chemical influences ...
Attention! The medical encyclopedia is provided on the site for informational purposes only, and is not a manual for self-treatment.
- Vertebrok.Ru is not responsible for the possible consequences of using the information provided in this section. Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor!
- Everything that can be purchased from us you can see at this link in the online store. Please do not call us about purchasing items that are not available in the online store.
Nail atrophy is one of the diseases of the nail, which is characterized by various types of deformation, from changes in the thickness of the nail to its structure. They are congenital (more often) and then associated with endocrine system disorders, or acquired consequences of certain dermatoses (lichen planus, psoriasis), which caused damage to the nail matrix.
Grooves, thimble-like or punctate surface, splitting and fragility of the edges may be due to vitamin deficiency. Trophic changes also occur with trauma (such are ingrown nails from too tight shoes), as well as with inflammation of the nail roller (panaritium). The appearance of white dots, transverse and longitudinal stripes on the nail plate is the result of an infection that has penetrated through an unsuccessfully removed (bitten) burr.
Symptoms
In most cases, acquired atrophy can affect all parts of one or more fingers. Affected nails are usually gray-white in color, their surface is dull, with flaws. The nail at the same time has a smaller size, it is thinner than healthy nails. The substance of the nail is soft, looks like a thickened membrane. The surface of the nail plate is rough, with longitudinal cracks, it looks like it has been worn off by worms.
Treatment:
Before prescribing therapy, patients should be carefully examined, paying special attention to age, the state of the nervous and endocrine systems, and the possibility of systematic traumatization of the nails. Treatment is prescribed depending on the underlying disease. In all cases, vitamins (especially A), preparations containing calcium, iron, zinc are shown.
Showing yeast, small doses of thyroidin, dieting. Locally - greasy creams, oils with corticosteroids. The rate of nail regrowth and the change in their properties towards improvement is affected by 20% metronidazole ointment. First, the nail is detached using ureaplast (1-2 sessions), and then this ointment is applied daily for 1-1.5 months.
Treatment of an ingrown nail is associated with the normalization of the functioning of its growth zone. For this you need:
build up the cuticle on the nail hole (do not push it back);
suppress inflammation: henceforth, it is correct to cut off the regrown edge of the nail - only parallel to the roller (the simplest trick is to lay a match over the edge of the nail and cut the nail exactly along it);
in the future, never wear uncomfortable shoes.
Nails are dense horny plates that protect the tissue of the nail bed from the effects of various chemical, thermal, and other environmental factors. The following parts of the nail are distinguished: the free (distal) edge, body, two lateral edges and the root part of the nail. In healthy people, the nail is smooth, colorless, slightly convex and largely transparent. Due to the translucence of numerous capillaries, the horny plate acquires a pink color.
The area and thickness of the nail depends on the normal activity of the body (gender, age), on the structure of the terminal phalanx of the fingers, and on the profession. Each person's nail surface pattern is unique and consists of longitudinal protrusions and depressions.
The growth and formation of the nail is determined by the activity of the matrix that makes up the root part. The rate of regrowth is individual, on average 0.1 mm per day. In women, nails grow somewhat more slowly than in men, in children faster than in adults. Complete nail regeneration takes an average of 170 days. In the fetus, the nails grow to the fingertips only by the end of the intrauterine period, so their length can be used to judge its full-term.
Violations in the color and structure of the nails are found in nervous, mental, endocrine and other systemic diseases. There are also groups of traumatic and occupational injuries, a number of anomalies can be congenital and hereditary.
Congenital absence of nails belongs to a group of rare hereditary anomalies. It can be manifested by the absence of one or more (all) nails and, as a rule, is combined with other disorders of the outer layer of the skin, sweat and sebaceous glands, changes in the structure of the hair and other malformations.Acquired anonychia occurs in organic diseases of the nervous system (taxus dorsalis, etc.), in injuries of the nail bed, and in some dermatoses (pemphigus, Duhring's disease, etc.). Tactics, therapy and prognosis of the disease determines the correct and timely diagnosis.
The processes of dystrophy can relate to their thickness, width, shape, consistency, from which nails appear flat, pterygoid, concave (spoon-shaped). They are congenital (more often) and then associated with endocrine system disorders, or acquired consequences of certain dermatoses (lichen planus, psoriasis), which caused damage to the nail matrix. Grooves, thimble-like or punctate surface, splitting and fragility of the edges may be due to vitamin deficiency. Trophic changes also occur with trauma (such are ingrown nails from too tight shoes), as well as with inflammation of the nail roller (panaritium). The appearance of white dots, transverse and longitudinal stripes on the nail plate is the result of an infection that has penetrated through an unsuccessfully removed (bitten) burr.Treatment. Before prescribing therapy, patients should be carefully examined, paying special attention to age, the state of the nervous and endocrine systems, and the possibility of systematic traumatization of the nails. Treatment is prescribed depending on the underlying disease. In all cases, vitamins (especially A), preparations containing calcium, iron, zinc are shown. Showing yeast, small doses of thyroidin, dieting. Locally - greasy creams, oils with corticosteroids. The rate of nail regrowth and the change in their properties towards improvement is affected by 20% metronidazole ointment. First, the nail is detached using ureaplast (1-2 sessions), and then this ointment is applied daily for 1-1.5 months.
Treatment of an ingrown nail is associated with the normalization of the functioning of its growth zone. To do this, it is necessary: a) to build up the cuticle on the nail hole (do not move it away); b) suppress inflammation: henceforth, it is correct to cut off the overgrown edge of the nail - only parallel to the roller (the simplest trick is to lay a match over the edge of the nail and cut the nail exactly along it); d) never wear uncomfortable shoes in the future.
A common type of nail dystrophy, in which the connection between the nail and the soft tissues of the bed is disrupted. Depending on the size of the detached part of the nail, partial and complete onycholysis is distinguished, more often in women.Its reasons are manifold. Traumatic develops as a result of mechanical, physical, chemical influences. Quite often, onycholysis occurs with eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, bullous dermatoses. Sometimes nail rejection occurs as a result of long-term use of tetracycline antibiotics. It can also be a symptom of systemic diseases, disorders of the cardiovascular, nervous, digestive systems, endocrinopathies and infectious diseases.
Treatment. It should be aimed primarily at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. In all cases, general strengthening agents are indicated (vitamin A, B, iron, calcium, etc.), taking gelatin in a daily dose of 5-7 g for 3-4 months. Hot and warm baths with potassium permanganate and overlay are recommended for local treatment. on the affected areas of the synthomycin emulsion, 5% heliomycin ointment (fixation with a sticky patch), the use of solutions (1-2% alcohol tinol, 5% chrysarobin in chloroform). Massage of the affected fingers has a beneficial effect.
Prevention. It consists in the hygienic maintenance of nails and protection from injury. Early contact with a doctor and treatment of comorbidities improve the prognosis.
Fungal infection of the nails is observed in patients with epidermophytosis of the feet, rubromycosis, chronic trichophytosis and favus (mainly on the hands), extremely rarely - with microsporia.Symptoms and course. Onychomycosis begins with the free or lateral edge of the nail. In its thickness, rounded and striped spots of yellowish, less often grayish-white color appear, which gradually merge with each other; the nail thickens, loosens, becomes brittle, crumbles. The process of destruction, slowly spreading, can capture the entire nail. At the same time, with rubromycosis of the nails of the hands, the plates may remain smooth and shiny, but undergo thinning or detachment from the bed; the exfoliated part acquires a dirty gray color.
Onychomycosis may be isolated; those. without damage to the skin and hair. Microscopic examination of pieces of affected nails reveals mycelial filaments.
Treatment of onychomycosis is a very complex process. The best method is combined - ingestion of griseofulvin (Nizoral) for 4-6 months, removal of nails and local fungicidal therapy. Nail removal can be done surgically or with keratolytic agents. There are several methods:
A) the method of Andriasyan G.K. - the affected nail is removed with onycholysin (15% barium sulfide on talc), which is applied to the nail in the form of a slurry for 30-40 minutes, moistening it all the time with water from a pipette. After that, the slurry is washed off with water, and the softened layer of the nail is scraped off with a scalpel, then onycholysin is reapplied and thus the entire nail is removed.
Next, an ointment of salicylic, lactic or benzoic acid and resorcinol, 15.0 g per 55.0 g of petroleum jelly, is applied to the nail bed under compress paper for 2 days. Exfoliated horny masses are removed with a scalpel and tweezers. They do 2-3 such rounds, after cleaning the nail bed is smeared with tincture of iodine until healthy nails grow back.
B) the method of Arabian A.N. - an ointment consisting of equal parts of potassium iodide and lanolin is applied to the affected nail for 10 days, until it softens.
After removal of such a nail, daily the nail bed is smeared with an ointment of the following composition: crystalline iodine 0.2 g, lanolin and potassium iodide 10.0 g each for 5 days.
These procedures are repeated several times.
C) the use of keratolytic patches - salicylic, trichloroacetic and "ureaplast", containing 20% urea.
Especially effective is ureaplast, which is applied to the affected nail after a preliminary hot soapy-soda bath with a thick layer of 3-5 cm and attached to the skin of the terminal phalanx with adhesive tape. The bandage is left for 5 days, and the procedure is repeated several times until the nail is completely softened. After removing the patch, the nail is removed with a scalpel, nail clippers or scissors. Next, local fungicidal therapy is prescribed, including patches - 20% pyrogallic, 5% salicylic-thymol, 5% betanaphthol, etc.
Local treatment of the nail bed should be continued for 4-6 months, i.e. until the nails grow back completely.
- disease of the nail fold caused by pyogenic microorganisms, see Ch. Surgical diseases. Changing their natural color.Various shades from white (leukonychia) to brown, red, green, blue and black can occur as a result of exposure to certain chemicals, dyes, varnishes, medications (antimalarial drugs, tetracycline antibiotics, drugs of silver, arsenic, phenolphthalein, gold, etc. .), accompany some skin, infectious, endocrine (diabetes, Addison's disease, gout) and internal (liver cirrhosis, anemia, heart disease, etc.) diseases.
Treatment. It should be aimed primarily at the possible elimination of the main cause of the disease, all kinds of intoxications, injuries and damage to the nail, its matrix and nail cuticle. It is useful to use vitamins, iron preparations, gelatin.
Toenail dystrophy (onychopathy) is a disease accompanied by a change in the shape, consistency and structure of the nail plates. The disease is equally common in men and women.
Usually, the pathology develops as a result of onychomycosis - an infectious lesion of the nails, but other factors can also provoke it, including trauma, vitamin deficiency, immunodeficiency, and much more.
Treatment of dystrophy of the nail plates is performed conservatively. The patient is prescribed certain drugs that restore the shape and consistency of the nails, strengthen the immune system, and prevent infectious inflammatory processes.
What is this article about?
Definition and causes of onychopathy
The nail is a horny plate, the density of which is provided by the peculiarities of the arrangement and adhesion of cells. Between the cells are the so-called keratin fibers.
Keratin layers contain water and fat molecules. It is fat that provides elasticity, flexibility and shine to nails. If there is a lack of water or fatty molecules in the nail plates, they become brittle and gradually deform.
Onychopathy is a disease in which the color, shape and consistency of the nail plates changes. This disease can be the result of many factors. Physicians refer to the main causes of dystrophy:
- Dermatoses and any other dermatological diseases.
- Nail fungus. With onychomycosis, the structure of the nail plates changes radically. They become thin, can exfoliate and crumble. In addition, pathogenic microorganisms cause local metabolic disorders, which only aggravates the situation.
- Mechanical damage to nails. Various cuts, bruises and any other injuries are fraught with onychopathy.
- Venereal diseases accompanied by immunodeficiency. Doctors say that the condition of the nails can be used to determine how strong a person’s immunity is without additional research. And there is some truth in these words. It has been proven that various immunodeficiency conditions contribute to onychopathy, including HIV, AIDS, chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.
- Diabetes. Hyperglycemia negatively affects metabolic processes, resulting in an increased likelihood of developing onychopathy.
- Avitaminosis and deficiency of important trace elements. In the absence of a sufficient amount of sulfur, calcium, vitamin A, B vitamins, zinc and magnesium in the diet, the nails will certainly begin to crumble and succumb to dystrophy.
- Acute disorders in the work of the organs of the cardiovascular system.
- Use of poor quality varnishes.
- Work with aggressive chemicals.
Often, onychopathy is a congenital disease. In this case, it is almost impossible to completely eliminate the disease.
Types and symptoms of onychopathy
Thinning and dystrophy of the nail plate as a whole can develop for a number of reasons, which we discussed above. Onychopathy itself is a generalizing concept. There are several types of the disease.
Each species has its own symptoms. The most common types are hapalonychia, onycholysis, onychorrhexis, onychoshisis, Beau-Reil's furrows, trachnonchinia, "thimble" nail, dyschromia, and manicure dystrophy.
Let's consider each type separately:
- Gapalonychia. This type of ailment is characterized by thinning of the nails, softening of the consistency, increased fragility. Externally, the nail plate becomes somewhat "raised". Pathology is often hereditary.
- Onycholysis. With this disease, the nail exfoliates and begins to be torn away from the nail bed. Hollows appear between the skin and the nail plates, the color of the nail also changes. Usually the affected plate acquires a yellowish tint.
- Onychorrhexis. It is characterized by longitudinal splitting of the nail plate. Cracks begin to spread, and over time, the nail simply falls off. In severe cases, pus is separated from the cracks.
- Onychoshisis. Accompanied by the formation of transverse cracks. The nail plates become gray or off-white. Sores may appear on the fingers. Onychoshisis most often develops in people whose work is closely associated with aggressive chemicals. When they enter the body of the nail plate, an inflammatory process develops, which ultimately causes dystrophy.
- Furrows of Beau-Reil. In this case, the so-called "furrows" appear on the nail plates. They are in the shape of an arc. The depth of the defect is 1-2 mm. The color of the affected nail, as a rule, does not change. But the plate takes on a wave-like shape.
- Trachnonchinia. It is characterized by "roughness" of the nail plates. The affected area changes in color. As a rule, the nail plate begins to delaminate completely. Most often, trachnonchinia develops against the background of eczema or.
- Thimble nail. A rare form of dystrophy. With this form of onychopathy, many dotted depressions form on the nail plates. The color of the affected area does not change. Interestingly, "thimbles" often occur against the background of seborrhea and with alopecia areata.
- Dyschromia. It develops with a lack of any macronutrients and vitamins, or as a result of injuries. Against the background of dyschromia, a change in the color of the nail plate is observed. Individual spots appear in the lesion, having a white, dark yellow or black color.
- Manicure dystrophy. The nail plate is covered with white stripes, begins to peel and thin, becomes brittle. The consistency of the plate itself also changes - the nail becomes rough.
Each type requires a specific approach to treatment.
How to cure toenail dystrophy?
With dystrophy of toenails, treatment is selected on an individual basis. Initially, the physician must find out the root cause of dystrophic processes, determine the type of onychopathy, and only then choose the tactics of treatment.
Diagnosis begins with an oral survey. Then a visual examination is performed, a scraping is done, if necessary, a biochemical and general blood test is prescribed. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the root cause of the pathological process.
But there are a number of general recommendations. First, the patient needs to give up bad habits. Smoking and alcoholism contribute to a decrease in immunity and disruption of the functionality of the cardiovascular system, so cigarettes and alcoholic beverages should be banned.
In addition, patients need:
- Eat a balanced diet. This is a necessary condition for recovery. The menu should include foods rich in protein, fiber, B vitamins, vitamin E, vitamin A, zinc, magnesium, selenium. You need to eat more vegetables, fruits, greens, lean meat, seafood.
- Observe the rules of hygiene. A secondary infection can get into the finger, or rather the affected nail plate. This will only make the situation worse. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend the use of antiseptics. Also at home, you can prepare therapeutic baths from oak bark, chamomile and calendula flowers.
- Attend physiotherapy sessions. They help strengthen the immune system, stimulate the growth of healthy nail plates, and prevent the complete destruction of the nail plate. Patients leave a lot of positive feedback about acupuncture, electrophoresis, mud therapy.
- Take multivitamin complexes. Medications based on vitamin E, B vitamins, vitamin A are prescribed. It is necessary to use the complexes for at least six months.
When secondary infections are attached, the treatment of nail dystrophy involves the use of antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol). Also, antifungal drugs may be recommended to the patient if the deformation of the plates was the result of exposure to dermatophytes, yeast, yeast-like microorganisms.
In such cases, antifungal lotions, ointments, gels, capsules or varnishes are prescribed. The best agents with fungicidal activity are Batrafen, Lotseril, Oflomil, Fluconazole.
Nail dystrophy is described in the video in this article.