How much smaller is the moon than the earth? Moon size, features, theory of origin and comparison with other celestial bodies of the solar system
Initially, there was an opinion that the Sun revolves around our planet, thereby illuminating each part of it in turn. But in the process of developing the science of astronomy, scientists nevertheless came to the truth that it is around the Sun that all objects in the solar system, including the Earth, rotate, and not vice versa.
Thanks to the radiation of this star, life is maintained, the process of photosynthesis occurs, during which oxygen is produced, which is so necessary for all living beings on the planet. But I wonder what is bigger: the Sun or the Earth?
Structure of the Sun

By studying the only star in the solar system, scientists came to a conclusion about its structure. The center is occupied by the nucleus. Its radius is approximately 150-175 thousand km. Helium is formed in the core as a result of continuously occurring nuclear reactions. Heat and energy are generated here; the rest of the star is heated due to the phenomenon of thermal exchange with the core. The energy, passing through all layers, is emitted from the photosphere in the form of bright sunlight.
It is by the upper layer of the Sun - the photosphere - that one can judge its size and distance to our planet.
The sun compared to the big stars

Structure of the Earth
The structure of the Earth is similar to that of the sun. The center of our planet is the core, the radius of which is approximately 3.5 thousand km. It is assumed that it consists of two parts, between which a so-called transition zone may periodically arise. In the central part there is a solid core with a radius of 1300 km, from the outside it is enveloped by a liquid outer core.
The mantle is the layer covering the Earth's core. And on top of the mantle there is a solid layer of the Earth - its surface, on which continents and oceans, mountains and depressions, land and water are located. The earth belongs to largest planets solar system. In 365 days, it manages to travel around the Sun and turn around its axis the same number of times. It is precisely due to which side our planet is turned to the star and the angle of inclination earth's axis, climate changes and daily alternation of days and nights are observed. The deviation of the axis from the vertical is 23.5 degrees.
In 1609, after the invention of the telescope, humanity was able to examine its space satellite in detail for the first time. Since then, the Moon has been the most studied cosmic body, as well as the first one that man managed to visit.
The first thing we have to figure out is what our satellite is? The answer is unexpected: although the Moon is considered a satellite, technically it is the same full-fledged planet as the Earth. She has big sizes- 3476 kilometers in diameter at the equator - and a mass of 7.347 × 10 22 kilograms; The Moon is only slightly inferior to the smallest planet in the Solar System. All this makes it a full participant in the Moon-Earth gravitational system.

Another such tandem is known in the Solar System, and Charon. Although the entire mass of our satellite is a little more than a hundredth of the mass of the Earth, the Moon does not orbit the Earth itself - they have a common center of mass. And the proximity of the satellite to us gives rise to another interesting effect, tidal locking. Because of it, the Moon always faces the same side towards the Earth.
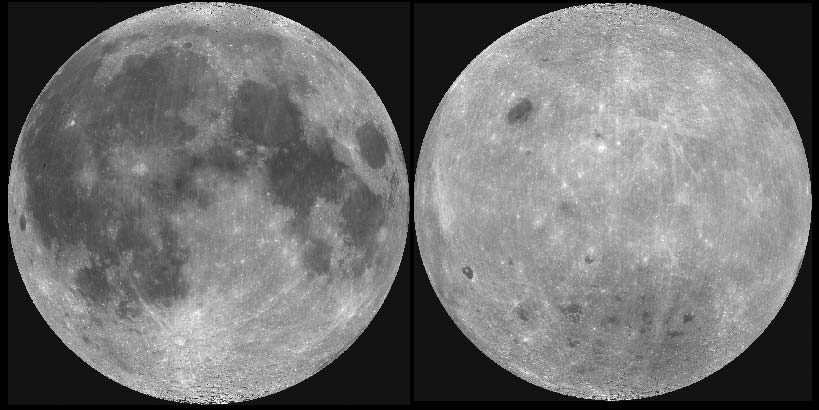
Moreover, from the inside, the Moon is structured like a full-fledged planet - it has a crust, a mantle and even a core, and in the distant past there were volcanoes on it. However, nothing remains of the ancient landscapes - over the course of four and a half billion years of the Moon’s history, millions of tons of meteorites and asteroids fell on it, furrowing it, leaving craters. Some of the impacts were so strong that they tore through its crust all the way to its mantle. The pits from such collisions formed the lunar seas, dark spots on the Moon, which are easily distinguishable from . Moreover, they are present exclusively on the visible side. Why? We will talk about this further.
Among cosmic bodies, the Moon influences the Earth the most - except, perhaps, the Sun. Lunar tides, which regularly raise water levels in the world's oceans, are the most obvious, but not the most strong impact satellite Thus, gradually moving away from the Earth, the Moon slows down the rotation of the planet - a solar day has grown from the original 5 to the modern 24 hours. The satellite also serves as a natural barrier against hundreds of meteorites and asteroids, intercepting them as they approach the Earth.

And without a doubt, the Moon is a tasty object for astronomers: both amateurs and professionals. Although the distance to the Moon has been measured to within a meter using laser technology, and soil samples from it have been brought back to Earth many times, there is still room for discovery. For example, scientists are hunting for lunar anomalies - mysterious flashes and lights on the surface of the Moon, not all of which have an explanation. It turns out that our satellite hides much more than is visible on the surface - let's understand the secrets of the Moon together!
Topographic map of the Moon
Characteristics of the Moon
Scientific study of the Moon today is more than 2200 years old. The movement of a satellite in the Earth's sky, phases and distance from it to the Earth were described in detail by the ancient Greeks - and internal structure The moon and its history are studied to this day by spacecraft. Nevertheless, centuries of work by philosophers, and then physicists and mathematicians, have provided very accurate data about how our Moon looks and moves, and why it is the way it is. All information about the satellite can be divided into several categories that flow from each other.

Orbital characteristics of the Moon
How does the Moon move around the Earth? If our planet were stationary, the satellite would rotate in an almost perfect circle, from time to time slightly approaching and moving away from the planet. But the Earth itself is around the Sun - the Moon has to constantly “catch up” with the planet. And our Earth is not the only body with which our satellite interacts. The Sun, located 390 times farther than the Earth from the Moon, is 333 thousand times more massive than the Earth. And even taking into account the inverse square law, according to which the intensity of any energy source drops sharply with distance, the Sun attracts the Moon 2.2 times stronger than the Earth!

Therefore, the final trajectory of our satellite’s motion resembles a spiral, and a complex one at that. The axis of the lunar orbit fluctuates, the Moon itself periodically approaches and moves away, and on a global scale it even flies away from the Earth. These same fluctuations lead to the fact that the visible side of the Moon is not the same hemisphere of the satellite, but its different parts, which alternately turn towards the Earth due to the “swaying” of the satellite in orbit. These movements of the Moon in longitude and latitude are called librations, and allow us to look beyond the far side of our satellite long before the first flyby by spacecraft. From east to west, the Moon rotates 7.5 degrees, and from north to south - 6.5. Therefore, both poles of the Moon can be easily seen from Earth.
The specific orbital characteristics of the Moon are useful not only to astronomers and cosmonauts - for example, photographers especially value the supermoon: the phase of the Moon in which it reaches maximum size. This is a full moon during which the Moon is at perigee. Here are the main parameters of our satellite:
- The Moon's orbit is elliptical, its deviation from a perfect circle is about 0.049. Taking into account orbital fluctuations, the minimum distance of the satellite to the Earth (perigee) is 362 thousand kilometers, and the maximum (apogee) is 405 thousand kilometers.
- The common center of mass of the Earth and the Moon is located 4.5 thousand kilometers from the center of the Earth.
- A sidereal month - the complete passage of the Moon in its orbit - takes 27.3 days. However, for a complete revolution around the Earth and change lunar phases it takes 2.2 days more - after all, during the time that the Moon moves in its orbit, the Earth flies a thirteenth part of its own orbit around the Sun!
- The Moon is tidally locked into the Earth - it rotates on its axis at the same speed as around the Earth. Because of this, the Moon is constantly turned to the Earth with the same side. This condition is typical for satellites that are very close to the planet.

- Night and day on the Moon are very long - half the length of an earthly month.
- During those periods when the Moon comes out from behind globe, it is visible in the sky - the shadow of our planet gradually slides off the satellite, allowing the Sun to illuminate it, and then covers it back. Changes in the illumination of the Moon, visible from the Earth, are called ee. During the new moon, the satellite is not visible in the sky; during the young moon phase, its thin crescent appears, resembling the curl of the letter “P”; in the first quarter, the Moon is exactly half illuminated, and during the full moon it is most noticeable. Further phases - the second quarter and the old moon - occur in the reverse order.

Interesting fact: since the lunar month is shorter than the calendar month, sometimes there can be two full moons in one month - the second is called a “blue moon”. It is as bright as an ordinary light - it illuminates the Earth by 0.25 lux (for example, ordinary lighting inside a house is 50 lux). The Earth itself illuminates the Moon 64 times stronger - as much as 16 lux. Of course, all the light is not our own, but reflected sunlight.
- The Moon's orbit is inclined to the Earth's orbital plane and regularly crosses it. The satellite's inclination is constantly changing, varying between 4.5° and 5.3°. It takes more than 18 years for the Moon to change its inclination.
- The Moon moves around the Earth at a speed of 1.02 km/s. This is much less than the speed of the Earth around the Sun - 29.7 km/s. The maximum speed of the spacecraft achieved by the Helios-B solar probe was 66 kilometers per second.
Physical parameters of the Moon and its composition

It took people a long time to understand how big the Moon is and what it consists of. Only in 1753, the scientist R. Bošković was able to prove that the Moon does not have a significant atmosphere, as well as liquid seas - when covered by the Moon, the stars disappear instantly, when their presence would make it possible to observe their gradual “attenuation”. It took another 200 years for the Soviet station Luna-13 to measure mechanical properties surface of the Moon. And nothing was known at all about the far side of the Moon until 1959, when the Luna-3 apparatus was able to take its first photographs.
The Apollo 11 spacecraft crew returned the first samples to the surface in 1969. They also became the first people to visit the Moon - until 1972, 6 ships landed on it and 12 astronauts landed. The reliability of these flights was often doubted - however, many of the critics' points were based on their ignorance of space affairs. The American flag, which, according to conspiracy theorists, “could not have flown in the airless space of the Moon,” is in fact solid and static - it was specially reinforced with solid threads. This was done specifically in order to take beautiful pictures - a sagging canvas is not so spectacular.

Many distortions of colors and relief shapes in the reflections on the helmets of the spacesuits in which counterfeits were sought were due to gold plating on the glass, which protected against ultraviolet. Soviet cosmonauts who watched the live broadcast of the astronaut landing also confirmed the authenticity of what was happening. And who can deceive an expert in his field?
And complete geological and topographic maps of our satellite are being compiled to this day. In 2009 space station LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter) not only delivered the most detailed images of the Moon in history, but also proved the presence of large quantity frozen water. He also put an end to the debate about whether people were on the Moon by filming traces of the activities of the Apollo team from low lunar orbit. The device was equipped with equipment from several countries, including Russia.

Since new space states like China and private companies are joining the lunar exploration, new data is arriving every day. We have collected the main parameters of our satellite:
- The surface area of the Moon occupies 37.9x10 6 square kilometers - about 0.07% of the total area of the Earth. Incredibly, this is only 20% greater than the area of all human-inhabited areas on our planet!
- The average density of the Moon is 3.4 g/cm 3 . It is 40% less than the density of the Earth - primarily due to the fact that the satellite is devoid of many heavy elements like iron, which our planet is rich in. In addition, 2% of the Moon's mass is regolith - small crumbs of rock created by cosmic erosion and meteorite impacts, the density of which is lower than normal rock. Its thickness is selected places reaches tens of meters!
- Everyone knows that the Moon is much smaller than the Earth, which affects its gravity. Acceleration free fall it is 1.63 m/s 2 - only 16.5 percent of the total gravitational force of the Earth. The astronauts' jumps on the Moon were very high, even though their spacesuits weighed 35.4 kilograms - almost like knight's armor! At the same time, they were still holding back: a fall in a vacuum was quite dangerous. Below is a video of the astronaut jumping from the live broadcast.
- Lunar maria cover about 17% of the entire Moon - mainly its visible side, which is covered by almost a third. They are traces of impacts from particularly heavy meteorites, which literally tore the crust off the satellite. In these places, only a thin, half-kilometer layer of solidified lava—basalt—separates the surface from the lunar mantle. Since closer to the center of any large cosmic body the concentration solids is growing, there is more metal in the lunar seas than anywhere else on the Moon.
- The main form of relief of the Moon is craters and other derivatives of impacts and shock waves from steroids. Huge lunar mountains and circuses were built and changed the structure of the surface of the Moon beyond recognition. Their role was especially strong at the beginning of the history of the Moon, when it was still liquid - the falls raised whole waves of molten stone. This also caused the formation of lunar seas: the side facing the Earth was hotter due to the concentration of heavy substances in it, which is why asteroids affected it more strongly than the cool back side. The reason for this uneven distribution of matter was the gravity of the Earth, which was especially strong at the beginning of the Moon’s history, when it was closer.

- In addition to craters, mountains and seas, there are caves and cracks in the moon - surviving witnesses of the times when the bowels of the Moon were as hot as , and volcanoes were active on it. These caves often contain water ice, like the craters at the poles, which is why they are often considered as sites for future lunar bases.
- The real color of the Moon's surface is very dark, closer to black. All over the Moon there are the most different colors- from turquoise blue to almost orange. The light gray tint of the Moon from the Earth and in the photographs is due to the high illumination of the Moon by the Sun. Due to its dark color, the surface of the satellite reflects only 12% of all rays falling from our star. If the Moon were brighter, during full moons it would be as bright as day.
How was the Moon formed?
The study of lunar minerals and its history is one of the most difficult disciplines for scientists. The surface of the Moon is open to cosmic rays, and there is nothing to retain heat at the surface - therefore, the satellite heats up to 105 ° C during the day, and cools down to –150 ° C at night. The two-week duration of day and night increases the effect on the surface - and as a result, the minerals of the Moon change beyond recognition with time. However, we managed to find out something.

Today it is believed that the Moon is the product of a collision between a large embryonic planet, Theia, and the Earth, which occurred billions of years ago when our planet was completely molten. Part of the planet that collided with us (and it was the size of ) was absorbed - but its core, along with part of the surface matter of the Earth, was thrown into orbit by inertia, where it remained in the form of the Moon.
This is proven by the deficiency of iron and other metals on the Moon, already mentioned above - by the time Theia tore out a piece of earthly matter, most of the heavy elements of our planet were drawn by gravity inward, to the core. This collision affected further development The Earth - it began to rotate faster, and its axis of rotation tilted, which made the change of seasons possible.
Then the Moon developed like an ordinary planet - it formed an iron core, mantle, crust, lithospheric plates and even its own atmosphere. However, the low mass and composition poor in heavy elements led to the fact that the interior of our satellite quickly cooled, and the atmosphere evaporated from high temperature and absence magnetic field. However, some processes inside still occur - due to movements in the lithosphere of the Moon, moonquakes sometimes occur. They represent one of the main dangers for future colonizers of the Moon: their scale reaches 5.5 points on the Richter scale, and they last much longer than those on Earth - there is no ocean capable of absorbing the impulse of the movement of the Earth’s interior.

Basic chemical elements on the Moon - these are silicon, aluminum, calcium and magnesium. The minerals that form these elements are similar to those on Earth and are even found on our planet. However, the main difference between the minerals of the Moon is the absence of exposure to water and oxygen produced by living beings, a high proportion of meteorite impurities and traces of the effects of cosmic radiation. Ozone layer The Earth was formed quite a long time ago, and the atmosphere burns most of the mass of falling meteorites, allowing water and gases to slowly but surely change the appearance of our planet.
Future of the Moon
The Moon is the first cosmic body after Mars that claims priority for human colonization. In a sense, the Moon has already been mastered - the USSR and the USA left state regalia on the satellite, and orbital radio telescopes are hiding behind the far side of the Moon from the Earth, a generator of a lot of interference on the air. However, what does the future hold for our satellite?
The main process, which has already been mentioned more than once in the article, is the moving away of the Moon due to tidal acceleration. It happens quite slowly - the satellite moves away no more than 0.5 centimeters per year. However, something completely different is important here. Moving away from the Earth, the Moon slows down its rotation. Sooner or later, a moment may come when a day on Earth will last as long as a lunar month - 29–30 days.

However, the removal of the Moon will have its limit. After reaching it, the Moon will begin to approach the Earth in turns - and much faster than it was moving away. However, it will not be possible to completely crash into it. 12–20 thousand kilometers from the Earth, its Roche lobe begins - the gravitational limit at which a satellite of a planet can maintain a solid shape. Therefore, the Moon will be torn into millions of small fragments as it approaches. Some of them will fall to Earth, causing a bombardment thousands of times more powerful than nuclear, and the rest will form a ring around the planet like . However, it will not be so bright - the rings of gas giants consist of ice, which is many times brighter than the dark rocks of the Moon - they will not always be visible in the sky. The ring of the Earth will create a problem for astronomers of the future - if, of course, there is anyone left on the planet by that time.
Colonization of the Moon
However, all this will happen in billions of years. Until then, humanity views the Moon as the first potential object for space colonization. However, what exactly is meant by “lunar exploration”? Now we will look at the immediate prospects together.
Many people think of space colonization as similar to New Age colonization of Earth - finding valuable resources, extracting them, and then bringing them back home. However, this does not apply to space - in the next couple of hundred years, delivering a kilogram of gold even from the nearest asteroid will cost more than extracting it from the most complex and dangerous mines. Also, the Moon is unlikely to act as a “dacha sector of the Earth” in the near future - although there are large deposits of valuable resources there, it will be difficult to grow food there.

But our satellite may well become a base for further space exploration in promising directions - for example, Mars. the main problem space exploration today means weight restrictions spacecraft. To launch, you have to build monstrous structures that require tons of fuel - after all, you need to overcome not only the gravity of the Earth, but also the atmosphere! And if this is an interplanetary ship, then it also needs to be refueled. This seriously constrains designers, forcing them to choose economy over functionality.
The moon is much better suited as a launch pad for spaceships. The lack of an atmosphere and low speed to overcome the Moon's gravity - 2.38 km/s versus 11.2 km/s on Earth - make launches much easier. And the satellite's mineral deposits make it possible to save on the weight of fuel - a stone around the neck of astronautics, which occupies a significant proportion of the mass of any apparatus. If we expand the production of rocket fuel on the Moon, it will be possible to launch large and complex spaceships, collected from parts delivered from Earth. And assembly on the Moon will be much easier than in low-Earth orbit - and much more reliable.

The technologies existing today make it possible, if not completely, then partially to implement this project. However, any steps in this direction require risk. The investment of huge amounts of money will require research for the necessary minerals, as well as the development, delivery and testing of modules for future lunar bases. And the estimated cost of launching even the initial elements alone can ruin an entire superpower!
Therefore, the colonization of the Moon is not so much the work of scientists and engineers, but of the people of the whole world to achieve such valuable unity. For in the unity of humanity lies the true strength of the Earth.
Dimensions of objects in the Universe in comparison (photo)
1. This is Earth! We live here. At first glance it is very large. But, in fact, compared to some objects in the Universe, our planet is negligible. Next photos will help you at least roughly imagine what just doesn’t fit in your head.
2. The location of planet Earth in the solar system.

3. Scaled distance between the Earth and the Moon. Doesn't look too far away, does it?

4. Within this distance you can place all the planets of our solar system, beautifully and neatly.

5. This little green spot is the mainland North America, on the planet Jupiter. You can imagine how much larger Jupiter is than the Earth.

6. And this photo gives an idea of the size of planet Earth (that is, our six planets) compared to Saturn.

7. This is what Saturn's rings would look like if they were around the Earth. Beauty!

8. Hundreds of comets fly between the planets of the solar system. This is what comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, on which the Philae probe landed in the fall of 2014, looks like, compared to Los Angeles.

9. But all objects in the solar system are negligible compared to our Sun.

10. This is what our planet looks like from the surface of the Moon.

11. This is what our planet looks like from the surface of Mars.

12. And this is us from Saturn.

13. If you fly to the edge of the solar system, you will see our planet like this.

14. Let's go back a little. This is the size of the Earth compared to the size of our Sun. Impressive, isn't it?

15. And this is our Sun from the surface of Mars.

16. But our Sun is only one of the stars in the Universe. Their number is greater than that of grains of sand on any beach on Earth.

17. This means that there are stars much larger than our Sun. Just look at how tiny the Sun is compared to the largest star known today, VY, in the constellation Canis Major.

18. But not a single star can compare with the size of our Milky Way Galaxy. If we reduce our Sun to the size of a white blood cell and reduce the entire Galaxy by the same amount, then Milky Way will be the size of Russia.

19. Our Milky Way Galaxy is huge. We live somewhere around here.

20. Unfortunately, all the objects that we can see with the naked eye in the sky at night are placed in this yellow circle.

21. But the Milky Way is far from the largest Galaxy in the Universe. This is the Milky Way compared to Galaxy IC 1011, which is 350 million light-years from Earth.

22. But that's not all. This Hubble image captures thousands upon thousands of galaxies, each containing millions of stars with their own planets.

23. For example, one of the galaxies in the photo, UDF 423. This galaxy is located ten billion light years from Earth. When you look at this photo, you are looking billions of years into the past.

24. This dark piece of the night sky looks completely empty. But when zoomed in, it turns out that it contains thousands of galaxies with billions of stars.

25. And this is the size of a black hole compared to the size of the Earth’s orbit and the orbit of the planet Neptune.

One such black abyss could easily suck in the entire solar system.